오늘은 class에 대해서 배워보도록 하겠습니다
| 목차 | |
| 1. | array 복습 |
| 2. | try ~ catch |
| 3. | class |
| 4. | 예제 문제 |
| 5. | 느낀 점 |
1. array 복습
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const memberObject = {
name: 'hong',
age: 30,
married: true,
favors: ["Baseball", "Game", "Movie", "etc..."]
};
const memberObject2 = {
name: 'kim',
age: 25,
married: false,
favors: ["Coffee", "Dog", "Movie", "etc..."]
};
const member = [];
member.push(memberObject);
/*
console.log(member);
console.log(member);
// memberObject를 3개 복사하여 저장
for(let i = 0; i < 3; i++){
member.push(memberObject);
}
console.log(member);
// 2번째 member를 kim으로 변경
member[1].name = 'kim';
console.log(member);
// memberObject는 하나의 객체 (다 똑같은 객체 -> class 생성)
*/
member.push(memberObject2);
console.log(member);
// 객체의 값을 전부 분해하여 콘솔에 찍기
// for of : 배열의 내용을 탐색할 때
// for in : 객체 안의 내용을 탐색할 때
// 객체 값을 출력 객체명[키명] = value 리턴
console.log(member[0].name);
console.log("-- 배열 객체 --");
for(let mem of member){
// 첫 번째 member 객체 값
for(let keyName in mem){
if(keyName == 'favors'){
console.log('--취미--');
for(let f of mem[keyName]){
console.log(f);
}
}else{
console.log(keyName+" : "+mem[keyName]);
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

▣ 리스트 출력하기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>내가 좋아하는 가수</h1>
<form action="">
이름 : <input type="text" id="name"><br>
나이 : <input type="text" id="age"><br>
주소 : <input type="text" id="address"><br>
playList : <br>
<input type="text" id="first">
<input type="text" id="second">
<input type="text" id="third">
<button type="button" id="add">등록</button>
</form>
<script>
const people = [];
const musician1 = {
name : '',
age : 0,
address : '',
playList : {
first : '',
second : '',
third : '',
}
}
const musician2 = {
name : '',
age : 0,
address : '',
playList : {
first : '',
second : '',
third : '',
}
}
const musician3 = {
name : '',
age : 0,
address : '',
playList : {
first : '',
second : '',
third : '',
}
}
let cnt = 0;
// people에 객체를 3개 등록
document.getElementById('add').addEventListener('click', ()=>{
cnt ++;
const name = document.getElementById('name').value;
const age = document.getElementById('age').value;
const address = document.getElementById('address').value;
const first = document.getElementById('first').value;
const second = document.getElementById('second').value;
const third = document.getElementById('third').value;
switch(cnt){
case 1:
console.log('-- 등록 --');
musician1.name = name;
musician1.age = age;
musician1.address = address;
musician1.playList.first = first;
musician1.playList.second = second;
musician1.playList.third = third;
console.log(musician1);
people.push(musician1);
break;
case 2:
musician2.name = name;
musician2.age = age;
musician2.address = address;
musician2.playList.first = first;
musician2.playList.second = second;
musician2.playList.third = third;
console.log(musician1);
people.push(musician2);
break;
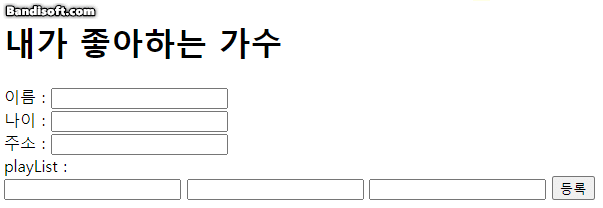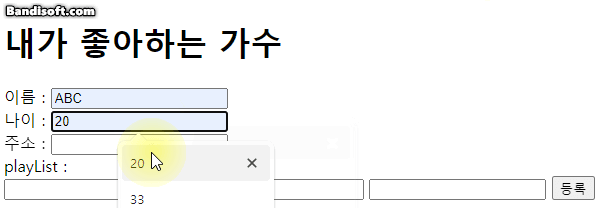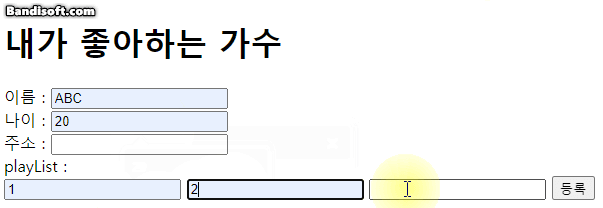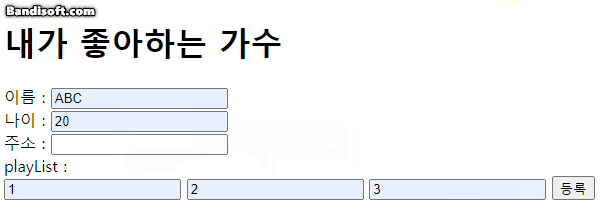
case 3:
musician3.name = name;
musician3.age = age;
musician3.address = address;
musician3.playList.first = first;
musician3.playList.second = second;
musician3.playList.third = third;
console.log(musician1);
people.push(musician3);
// 3명의 데이터를 콘솔에 for문으로 순회 나열
console.log("-- 배열 객체 --");
for(let result of people){
for(let keyName in result){
if(keyName == 'playList'){
console.log('-- playList --');
// 다시 객체 안
for(let key in result[keyName]){
console.log(result[keyName][key]);
}
}else{
console.log(keyName + ' : ' + result[keyName]);
}
}
console.log('----------');
}
break;
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

2. try ~ catch
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
try~catch : 예외 처리 프로세스
예상되는 에러를 try{code...} 영역에 배치를 하고, 만약 에러가 발생하면,
catch(err){code...} 영역에서 처리하는 예외처리 프로세스
</h1>
<ul>
<li>
try 영역 : 에러가 발생할 수 있는 코드를 실행
자바 스크립트에서 에러가 발생하면 에러 발생 라인부터 동작이 멈춤.
에러가 발생해도 다음 코드로 넘어감
</li>
<li>
catch(err){ } : 에러가 발생하면 예외처리를 하는 곳
</li>
<li>
try~catch로 예외처리를 하면 프로세스가 멈추지 않고, 지속시킬 수 있음
</li>
<li>
finally 영역: 예외처리와 상관없이 무조건 실행되어야 하는 코드를 넣는 영역
</li>
<li>
throw : 예외를 고의적으로 발생시키는 키워드 throw + 예외발생 후 처리코드
</li>
</ul>
<script>
console.log('프로세스 시작');
let num = 0;
try{
alert('경고창');
throw new '경고창 에러시 문구';
console.log(10 + num);
console.log(10 - num);
}catch(err){
console.log(err.name);
console.log(err.message);
}finally{
console.log("꼭 출력되어야 하는 문구");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

3. class
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
클래스, 생성자, 객체
</h1>
<!--
클래스는 생성 기본 문법
- 클래스는 반드시 첫 글자 대문자
class MyClass{
//생성자 : 자바 스크립트의 생성자는 1개만 허용
constructor(param){
...
}
//method 정의
methodName(param){
...
}
methodName(param){
...
}
// getter / setter
get name() {
return this.name;
}
set name(value){
this.name = value;
}
}
-->
<script>
class Car{
constructor(name, year){
this.name = name;
this.year = year;
this.model = '';
}
}
let myCar1 = new Car('쏘나타', 2023);
myCar1.model = "XG";
console.log(myCar1);
let myCar2 = new Car('그랜저', 2022);
console.log(myCar2);
let myCar3 = new Car();
myCar3.name = '아반떼';
myCar3.year = 2024;
myCar3.model = 'XD';
consol.log(myCar3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// class 객체 생성 / 일반 객체 생성
// 계좌 이름, 금액, 입금, 출금, 이체
// 일반 객체 생성
const myAccount = {
name : 'hong',
balance : 0,
//입금
deposit: function(amount){
this.balance += amount; // 누적
},
//출금
withdraw: function(amount){
this.balance -= amount;
},
//이체
transfer: function(amount, otherAccount){
this.balance -= amount;
otherAccount.balance += amount;
}
}
const yourAccount = {
name : 'kim',
balance : 10000,
//입금
deposit: function(amount){
this.balance += this.amount; // 누적
},
//출금
withdraw: function(amount){
this.balance -= amount;
},
//이체
transfer: function(amount, otherAccount){
this.balance -= amount;
otherAccount.balance += amount;
}
}
console.log(myAccount.name, ":", myAccount.balance);
myAccount.deposit(10000);
console.log(myAccount.name, ":", myAccount.balance);
myAccount.withdraw(3000);
console.log(myAccount.name, ":", myAccount.balance);
myAccount.transfer(2000, yourAccount);
console.log(myAccount.name, ":", myAccount.balance);
console.log(yourAccount.name, ":", yourAccount.balance);
console.log('--------------------');
//class로 객체 생성
class BankAccount{
constructor(name, balance){
this.name = name;
this.balance = balance;
}
//입금
deposit(amount){
this.balance += amount; // 누적
return this.balance;
}
//출금
withdraw(amount){
this.balance -= amount;
return this.balance;
}
//이체
transfer(amount, otherAccount){
this.balance -= amount;
otherAccount.balance += amount;
return this.balance;
}
}
let leeAcc = new BankAccount('lee', 5000);
let choiAcc = new BankAccount('choi', 10000);
console.log(leeAcc.name, ":", leeAcc.balance);
console.log(choiAcc.name, ":", choiAcc.balance);
console.log(leeAcc.deposit(10000));
console.log(leeAcc.name, ":", leeAcc.balance);
console.log(leeAcc.withdraw(3000));
console.log(leeAcc.transfer(10000, choiAcc));
console.log(choiAcc.name, ":", choiAcc.balance);
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

◈ get, set
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 생성자 함수 : 클래스의 함수화
// class, 생성자함수, 객체
// 일반 함수와 생성자 함수는 별반 차이가 없음.
// 1. 반드시 new를 통해 실행
// 2. 반드시 함수 첫 글자를 대문자로 시작
class PersonClass{
constructor(first, last, age, addr){
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
this.age = age;
this.addr = addr;
}
get personInfo(){
return `${this.firstName}, ${this.lastName} (${this.age}) : ${this.addr}`;
}
}
// get을 호출시 ()가 없음.
const my = new PersonClass('kim', 'minji', 20, 'seoul');
console.log(my);
console.log(my.personInfo);
// 위의 클래스를 생성자 함수로 변환
function PersonObject(first, last, age, addr){
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
this.age = age;
this.addr = addr;
this.getPersonInfo = function(){
return `${this.firstName}, ${this.lastName} (${this.age}) : ${this.addr}`;
}
}
const my2 = new PersonObject('lee', 'minji', 23, 'seoul');
console.log(my2);
console.log(my2.getPersonInfo());
// 객체로 생성
const person = {
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
age: '',
address: '',
setInfo: function(first, last, age, addr){
this.firstName = first;
this.lastName = last;
this.age = age;
this.addr = addr;
},
get personInfo(){
return `${this.firstName}, ${this.lastName} (${this.age}) : ${this.addr}`;
},
set setFirstName(first){
this.firstName = first;
}
};
person.setInfo('park', 'minji', 25, 'seoul');
console.log(person);
// get, set은 둘 다 ()가 없음.
console.log(person.PersonInfo);
// set 설정
person.setFirstName = 'lee';
console.log(person.PersonInfo);
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

▣ 나이 출력
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// class User 생성
// name, birth를 받아서 멤버변수로 저장
// get age() 나이를 리턴
// status() 성인인지 미성년자인지 리턴 (콘솔에 출력)
let day = new Date();
today = Number(day.toLocaleDateString());
let check = 0;
class User{
constructor(name, birth){
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
get age(){
let birthday = new Date(this.birth);
let todayYear = new Date().getFullYear();
return todayYear - birthday.getFullYear();
}
status(){
if(this.age < 20){
return '미성년자';
}else{
return '성인';
}
}
}
const hong = new User('hong', '2009-09-30');
console.log(hong.age);
console.log(hong.status());
const kim = new User('kim', '1990-01-01');
console.log(kim.age);
console.log(kim.status());
</script>
</body>
</html>
▷ 출력

4. 예제 문제
◎ 문제
▶ 1번

◎ 정답
▶ 1번
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 구구단 문제 -->
<h1>
<button type="button" id="startBtn">문제출제</button>
</h1>
<ol id="q"></ol>
<h1>
<button type="button" id="compareBtn">정답확인</button>
</h1>
<h3 id="printRatio"></h3>
<script>
//input.style.backgroundColor = 'green'
//style을 객체의 속성으로 줄 때 camelCase로 변경하여 속성을 줌.
//정답 Object ans1 ans2 ...
const ansObj = {}; //정답을 담을 객체
//ansObj[`ans${i}`] = dan * incre;
let quizArea = document.getElementById('q');
let count=0; //전체개수
let correct = 0; //정답개수
document.getElementById('compareBtn').addEventListener('click',()=>{
correct=0;
count=0;
while(count < 10){
count++;
// let userInput = document.getElementById(`userAns${count}`);
let userInput = document.getElementById('userAns'+count);
if(userInput.value == ansObj[`ans${count}`]){
correct++;
userInput.value += " : 정답!!";
userInput.style.backgroundColor = 'green';
}else{
userInput.value += " : 오답!!";
userInput.style.backgroundColor = 'red';
}
}
document.getElementById('printRatio').innerText =
`정답갯수 : ${correct}, 정답률 : ${(correct/count).toFixed(2)*100}%`;
});
document.getElementById('startBtn').addEventListener('click',()=>{
count=0;
document.getElementById('printRatio').innerText = "";
let q = '';
do{
count++;
let dan = Math.floor(Math.random()*8)+2;
let incre = Math.floor(Math.random()*9)+1;
let answer = dan * incre;
ansObj[`ans${count}`] = answer; //object에 정답 추가
//값 뿌리기
q+= `<li>${dan} * ${incre} = <input type="text" id="userAns${count}"> </li>`;
}while(count < 10);
quizArea.innerHTML = q;
console.log(ansObj);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
5. 느낀 점
구구단 문제를 풀 때 innerHTML를 이용해 input을 여러 개 생성을 하려는 파트에서 똑같은 id가 여러 개이면 인지를 못한다는 점을 몰라서 제대로 풀 지 못했었다. 오늘 내용을 복습하면서 ``, ${}를 중심으로 공부해야겠다고 생각했다.
'Front-end > Js' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Js 기초(BOM, DOM, classList)- AWS 풀스택 과정 23일차 (0) | 2024.08.14 |
|---|---|
| Js 기초(JSON, AJAX)- AWS 풀스택 과정 22일차 (0) | 2024.08.13 |
| Js 기초(set, map)- AWS 풀스택 과정 20일차 (0) | 2024.08.09 |
| Js 기초(array)- AWS 풀스택 과정 19일차 (0) | 2024.08.08 |
| Js 기초(if, for)- AWS 풀스택 과정 18일차 (0) | 2024.08.07 |