| 목차 | |
| 1. | 실습 |
| 2. | extends |
| 3. | abstract |
| 4. | 느낀 점 |
1. 실습
▣ Student
package day04;
/* - 학생 정보를 관리하기 위한 클래스
* - 학생 기본정보 : 이름, 생년월일, 전화번호, 나이
* - 학원 정보 : 학원명 = "EZEN" (final static), wlwja
* - 수강 정보 : 수강과목, 기간
* => 여러 과목을 들을 수 있음.(여러 과목을 수강하기 위해서는 배열로 처리 / 5과목까지 가능)
*
* ex) 홍길동(010101) 010-1111-1111 / 25 -> 학생정보
* EZEN(인천) -> 학원정보
* 자바 6개월, 파이썬 1개월, SQLD 1개월 -> 수강정보
* 기능(메서드)
* - 학생의 기본정보를 출력하는 기능
* - 학원 정보를 출력하는 기능
* - 수강정보를 출력하는 기능
* - 학생이 수강정보를 추가하는 기능
*/
public class Student {
// 멤버변수 선언
// 이름, 생년월일, 전화번호, 나이
private String name;
private String birth;
private String phone;
private String age;
// 학원명 "EZEN" (final static), 지정
private final static String COMPANY="EZEN";
private String branch;
// 수강과목, 기간
private String [] course = new String[5];
private String [] period = new String[5];
// index처리용 변수
private int cnt;
// 생성자
public Student() {
}
// phone, branch, name
public Student(String name, String phone, String branch) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.branch = branch;
}
public Student(String name, String birth, String phone, String age, String branch) {
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
this.phone = phone;
this.age = age;
this.branch = branch;
}
// method
/*
* - 학생의 기본정보를 출력하는 기능
* - 학원 정보를 출력하는 기능
* - 수강정보를 출력하는 기능
* - 학생이 수강정보를 추가하는 기능
*/
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("--학생정보--");
System.out.println(name+"("+birth+")"+phone+"/"+age);
}
public void printCompany() {
System.out.println(COMPANY+"/"+branch+"지점");
}
// 수강정보 출력
public void printCourse() {
if(course.length == 0 || cnt == 0) {
System.out.println("수강과목이 없습니다.");
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
System.out.print(course[i]+"("+period[i]+") ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 수강등록
// insertCourse()
// 매개변수 : 등록하고자 하는 course, period
// 리턴타입 : 배열에 데이터 추가 (리턴되는 값은 없음) void
public void insertCourse(String course, String period) {
// cnt가 0인 상황 (하나도 추가되지 않은 상황)
if(cnt >= 5) {
System.out.println("더이상 수강하실 수 없습니다.");
// 배열을 늘려서 더많은 수강을 받을 수도 있음.(배열복사)
return;
}
this.course[cnt] = course;
this.period[cnt] = period;
cnt++;
}
// getter / setter
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(String birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getBranch() {
return branch;
}
public void setBranch(String branch) {
this.branch = branch;
}
public String[] getCourse() {
return course;
}
public void setCourse(String[] course) {
this.course = course;
}
public String[] getPeriod() {
return period;
}
public void setPeriod(String[] period) {
this.period = period;
}
public int getCnt() {
return cnt;
}
public void setCnt(int cnt) {
this.cnt = cnt;
}
public static String getCompany() {
return COMPANY;
}
}
▣ StudentMain
package day04;
import day04.Student;
public class StudentMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("홍길동");
s.setPhone("010-1111-1111");
s.printInfo();
s.printCompany();
s.printCourse();
Student s1 = new Student("hong", "010-1111-2222", "incheon");
s1.printInfo();
s1.printCompany();
s1.insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
s1.insertCourse("python", "1 Month");
s1.printCourse();
Student s2 = new Student("park", "010101", "010-2222-2222", "25", "seoul");
s2.printInfo();
s2.printCompany();
s2.insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
s2.insertCourse("HTML", "1 Month");
s2.insertCourse("React", "1 Month");
s2.printCourse();
Student[] std = new Student[8];
std[0] = s;
std[1] = s1;
std[2] = s2;
// 5명 정보를 추가
std[3] = new Student("kim", "010202", "010-2222-3333", "25", "incheon");
std[3].insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
std[3].insertCourse("HTML", "1 Month");
std[3].insertCourse("React", "1 Month");
std[4] = new Student("choi", "010206", "010-2222-3333", "24", "seoul");
std[4].insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
std[4].insertCourse("HTML", "1 Month");
std[4].insertCourse("React", "1 Month");
std[5] = new Student("lee", "030502", "010-2222-3333", "23", "incheon");
std[5].insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
std[5].insertCourse("HTML", "1 Month");
std[5].insertCourse("React", "1 Month");
std[6] = new Student("kang", "020506", "010-2222-3333", "22", "seoul");
std[6].insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
std[6].insertCourse("HTML", "1 Month");
std[6].insertCourse("React", "1 Month");
std[7] = new Student("ha", "000207", "010-2222-3333", "21", "seoul");
std[7].insertCourse("java", "5 Month");
std[7].insertCourse("HTML", "1 Month");
std[7].insertCourse("React", "1 Month");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------");
// 학생 전체 명단 출력 (학생정보만)
for(int i = 0; i < std.length; i++) {
std[i].printInfo();
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------");
// hong 학생의 학생정보, 학원정보, 수강정보 출력
String searchName = "hong";
for(int i = 0; i < std.length; i++) {
if (std[i].getName().equals(searchName)) {
std[i].printInfo();
std[i].printCompany();
std[i].printCourse();
}
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------");
// incheon 지점의 학생 명단 출력 (학생정보만)
String searchBranch = "incheon";
for(int i = 0; i < std.length; i++) {
if(std[i].getBranch() != null) { // nullPointException 방지용
if (std[i].getBranch().equals(searchBranch)) {
std[i].printInfo();
}
}
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------");
// java 과목을 수강하는 학생명단 출력(학생정보, 학원정보, 수강정보전부 출력)
String searchCourse = "java";
System.out.println("---"+searchCourse+"과목 수강학생 정보---");
//전체 학생 배열에서 개개인의 과목 배열로 2중 검색
int cnt=0;
while(cnt < std.length) {
for(int i=0; i<std[cnt].getCourse().length; i++) {
if(std[cnt].getCourse()[i] != null) {
if(std[cnt].getCourse()[i].equals(searchCourse)) {
std[cnt].printInfo();
std[cnt].printCompany();
std[cnt].printCourse();
}
}
}
cnt++;
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------");
// 수강하지 않는 학생 명단 출력 (학생정보만)
System.out.println("---수강과목이 없는 학생 정보---");
cnt=0;
while(cnt < std.length) {
if(std[cnt].getCourse()[0] == null) {
std[cnt].printInfo();
}
cnt++;
}
}
}
▷ 출력
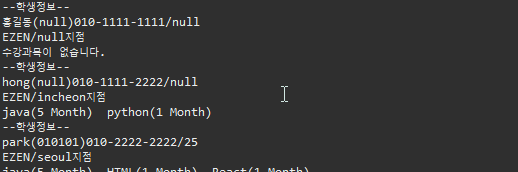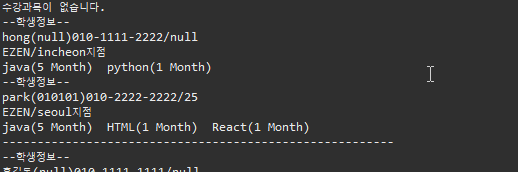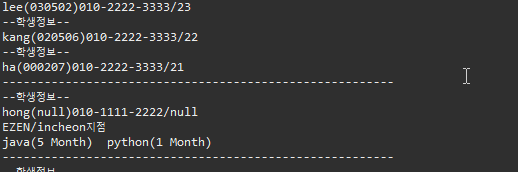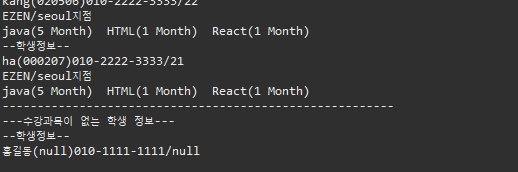
2. extends
■ 이론







▣ Extends01
※ Override 자동 생성
Source - Override / Implement Methods ...
package day04;
class A{
private int a, b, c; // 나만 사용 가능
protected int num1; // 상속가능
public void print() {
System.out.println("a:"+a+", b:"+b+", c:"+c);
System.out.println(" num1:"+num1);
}
public int getA() {
return a;
}
public int getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(int b) {
this.b = b;
}
public int getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(int c) {
this.c = c;
}
public int getNum1() {
return num1;
}
public void setNum1(int num1) {
this.num1 = num1;
}
public void setA(int a) {
this.a = a;
}
}
class B extends A {
private int d, e, f;
// 오버라이드(override) : 부모의 메서드를 재정의하여 사용하는 것
// super : 부모의 멤버값을 가져올 때 사용하는 키웓
@Override
public void print() {
super.print(); // 부모의 메서드를 호출하여 가져오기
System.out.println("d: "+d+", e: "+e+", f: "+f);
}
public int getD() {
return d;
}
public void setD(int d) {
this.d = d;
}
public int getE() {
return e;
}
public void setE(int e) {
this.e = e;
}
public int getF() {
return f;
}
public void setF(int f) {
this.f = f;
}
}
public class Extends01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 상속(Inheritance) : 부모 클래스의 멤버 요소를 자식이 물려받는 것.
* 멤버 요소 : 멤버변수, 메서드 사용가능. private은 상속 안 됨.
* 상속받는 부모클래스가 다른 패키지에 있다면 default도 상속대상이 안 됨.
* public / protected 접근제한자만 가능
*
* 상속 키워드 : extends
* 상속은 1개만 가능. 다중 상속을 허용하지 않음.
*
* class 자식class명 extends 부모class명 extends X {
* 본인의 멤버변수와 메서드 구현 가능.
* 본인멤버변수+본인메서드+부모멤버변수+부모메서드
* }
*/
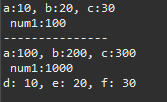
A a = new A(); // 부모 클래스의 객체 생성
a.setA(10);
a.setB(20);
a.setC(30);
a.setNum1(100);
a.print();
System.out.println("---------------");
B b = new B();
b.setA(100);
b.setB(200);
b.setC(300);
b.num1 = 1000; // 접근제한자가 protected라서 직접 접근 가능.
b.setD(10);
b.setE(20);
b.setF(30);
b.print();
}
}
▷ 출력
▣ Extends02
package day04;
class Animal{
// 동물의 이름과 종류를 나타내는 클래스
// 메서드 : 이름과 종류를 출력하는 메서드, 동물의 울음소리를 출력하는 메서드
private String name;
private String category;
public Animal() {}
public Animal(String name, String category){
this.name = name;
this.category= category;
}
//출력메서드
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("이름:"+name+" / 종류:"+category);
}
//울음소리 메서드
public void howl() {
System.out.println("--"+name+"의 울음소리");
// 나머지는 자식이 구현
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
// Dog, Cat Animal 클래스를 상속받아 생성
// printInfo() / howl() : 오버라이딩 후 본인의 울음소리를 추가해서 출력
class Dog extends Animal{
//생성자
public Dog() {
setName("강아지");
setCategory("개과");
}
@Override
public void howl() {
super.howl(); //부모의 howl() 메서드 값
System.out.println("왈왈!!");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name, String category) {
super.setName(name);
super.setCategory(category);
}
@Override
public void howl() {
super.howl();
System.out.println("그릉그릉..");
}
}
class Tiger extends Animal{
public Tiger(String name, String category) {
super(name, category); //부모 생성자 호출
}
@Override
public void howl() {
super.howl();
System.out.println("어흥~!!");
}
}
public class Extends02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 오버라이딩 : 부모클래스의 메서드를 재정의하여 사용하는 것
// - 부모클래스의 메서드와 선언부가 일치해야 함. { 구현만 재정의 가능. }
// - 접근제한자는 더 넓은 범위만 가능, 축소는 안됨.
Dog d = new Dog();
d.printInfo();
d.howl();
System.out.println("-------------------------");
Cat c = new Cat("나비", "고양이과");
c.printInfo();
c.howl();
System.out.println("--------------------------");
Tiger t = new Tiger("산신", "고양이과");
t.printInfo();
t.howl();
}
}
▷ 출력

3. abstract
■ 이론


▣ Abstract01
package day04;
// 추상클래스
abstract class Animal1{
protected String name;
protected String category;
// 일반 메서드
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println(name+"("+category+")");
}
// 추상 메서드
abstract public void howl();
}
class Dog1 extends Animal1{
private String eat; // 먹이종류
public Dog1(String name, String category) {
// protected라서 set 없이 바로 접근 가능
super.name = name;
super.category = category;
}
@Override
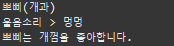
public void howl() {
System.out.println("울음소리 > 멍멍");
}
public void eating(String eat) {
this.eat = eat;
System.out.println(name+"는 "+eat+"을 좋아합니다.");
}
}
public class Abstract01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog1 d = new Dog1("뽀삐","개과");
d.printInfo();
d.howl();
d.eating("개껌");
/* 추상클래스 : 미완성 클래스, 추상메서드를 포함하는 클래스
* 추상클래스 요소 : 멤버변수 + 상수(final) + 일반메서드 + 추상메서드
* 추상클래스 : 객체를 생성할 수 없다. 반드시 추상메서드를 구현하여 완성해야 객체를 생성
* 추상메서드 : 메서드의 선언부만있고, 구현이 없는 메서드
* 추상 키워드 : abstract
* abstract class Animal {}
* abstract public void howl(매개변수); // 추상메서드
* - 추상클래스에 abstract 키워드는 반드시 포함해야 함.
* - 인터페이스는 추상메서드를 포함해도 abstract 키워드 생략가능
* - 상속받은 클래스에 추상메서드가 있다면 반드시 구현
*/
}
}
▷ 출력
▣ 과제
package day04;
import java.util.Scanner;
/* Product 클래스 생성 : 상품을 등록하는 클래스
* 상품명(name), 가격(price)을 멤버변수로 생성
* 상품을 추가 메서드
* 상품출력 메서드 (toString 이용)
* ex) 사탕 : 500
* 과자 : 2000
* 젤리 : 1000
*/
class Product {
private String name = new String();
private String price = new String();
private int cnt;
public Product() {}
private String [] ProductList = new String[10];
@Override
public String toString() {
System.out.println("--상품정보--");
return "[" + name + " : " + price + "]";
}
// public void printList() {
// if(ProductList.length == 0 || cnt == 0) {
// System.out.println("상품이 없습니다.");
// return;
// }
// for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
// System.out.print(ProductList[i]);
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
public void Scanner(String name, String price) {
if(cnt >= 10) {
System.out.println("더이상 수강하실 수 없습니다.");
return;
}
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
cnt++;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
public class 과제 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 상품 10개를 등록할 수 있는 배열 생성
* 스캐너를 통해 상품을 등록
* 등록한 상품을 출력
* 상품을 등록하시겠습니까? (y/n) y => 등록 n => 그만
*/
Product[] p = new Product[10];
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean check = true;
int cnt = 0;
String word = "";
String word1 = "";
String word2 = "";
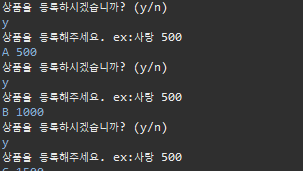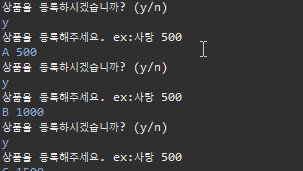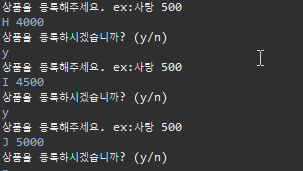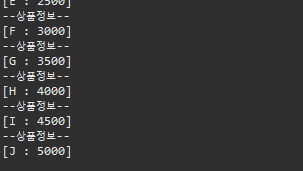
do {
System.out.println("상품을 등록하시겠습니까? (y/n)");
word = scan.next();
if(word.equals("y")) {
System.out.println("상품을 등록해주세요. ex:사탕 500");
word1 = scan.next();
word2 = scan.next();
if(cnt == 10) {
System.out.println("상품을 다 등록했습니다.");
}else if(word1 != null && word2 != null) {
Product a = new Product();
a.Scanner(word1, word2);
p[cnt] = a;
cnt++;
}
}else {
System.out.println("종료합니다.");
check = false;
}
}while(check);
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
System.out.println(p[i].toString());
}
scan.close();
}
}
▷ 출력
4. 느낀 점
이중구문이 너무 어려웠던 것 같다. 복습을 열심히 해야겠다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java 기초(실습)- AWS 풀스택 과정 50일차 (3) | 2024.10.04 |
|---|---|
| Java 기초(interface)- AWS 풀스택 과정 49일차 (4) | 2024.10.02 |
| Java 기초(class)- AWS 풀스택 과정 47일차 (1) | 2024.09.27 |
| Java 기초(method)- AWS 풀스택 과정 46일차 (2) | 2024.09.26 |
| Java 설정 및 기초- AWS 풀스택 과정 45일차 (4) | 2024.09.25 |