| 목차 | |
| 1. | Thread |
| 2. | Signeton |
| 3. | DB 연결 |
1. Thread
▣ Thread01
package day11;
public class Thread01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Thread(쓰레드) : 실제 작업을 수행하는 단위
* - 프로그램이 실행되면 OS로부터 메모리를 할당 받아 process의 상태 됨
* - 하나의 process는 하나 이상의 Thread를 가지게 됨
* - Thread는 실제 작업을 수행하는 단위이다
* - thread가 실제 CPU가 작업을 처리하는 단위
* - multi-thread : 여러 개의 thread가 동시에 수행되는 프로그램
* - CPU는 시간을 잘게 쪼개서 threa를 번갈아 수행함. (시분할 처리)
* - thread는 각자 자신만의 작업공간을 가짐 (context)
* - 각 thread는 공유하는 자원이 있을 수 있음. (자바에서는 static instance)
* - 여러 thread가 공유하는 자원을 사용하려고 경쟁이 발생함
* - 경쟁이 발생하는 구역 critical section(임계영역)
* - 임계영역에서 교착상태(deadlock)가 발생하지 않도록 동기화(순차적 수행) 구현하여 오류를 막음.
*/
/* Thread를 구현하는 2가지 방법
* 1. Thread 클래스를 상속하여 만들기
* 2. Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하여 만들기
* 자바는 다중상속을 허용하지 않기 때문에, 다른 클래스를 상속 중이라면 2번으로 구현
*/
// 현재 실행중인 스레드 이름
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
MyThread th = new MyThread();
th.start(); // run() 메서드 실행
MyThread th2 = new MyThread();
th2.start();
System.out.println("thread end~!!");
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread{
// 반드시 run()이라는 메서드를 구현해야 함.
@Override
public void run() {
// 0 ~ 500까지 반복하여 실행하는 구문수행
for(int i = 0; i <= 500; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "번째 thread > " + getName());
}
}
}
▷ 출력
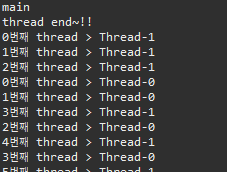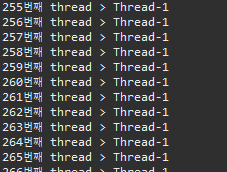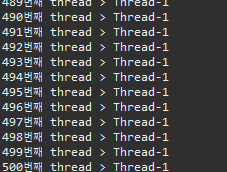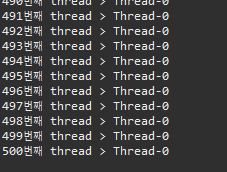
▣ Thread02
package day11;
class MyThread2 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// run은 반드시 구현해야 함
// 0 ~ 500까지 반복하여 실행하는 구문수행
for (int i = 0; i <= 500; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "번째 thread > " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}
public class Thread02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2. runnable 구현하는 방법
// join() : 동시에 여러 개의 스레드가 실행될 때 다른 스레드의 결과를
// 참조하여 실행되어야 할 경우 join() 메서드를 사용
// join() : try~catch 필요
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("main thread start");
MyThread2 th2 = new MyThread2();
Thread th = new Thread(th2);
th.start();
try {
th.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread th3 = new Thread(new MyThread2());
th3.start();
try {
th3.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main thread end");
}
}
▷ 출력
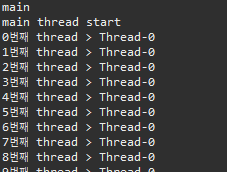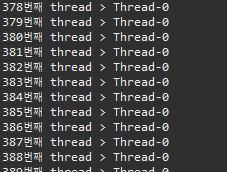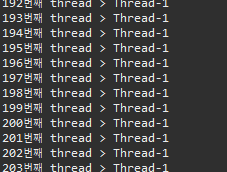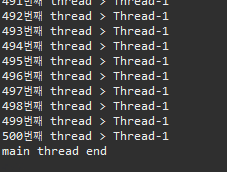
▣ Thread03
package day11;
class JoinTest extends Thread{
int start;
int end;
int total;
public JoinTest(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
this.total += i;
}
}
}
public class Thread03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1 ~ 50, 51 ~ 100까지의 합을 구하는 두 개의 Thread를 생성
// 그 결과를 확인
// Thread.sleep() : 기다렸다가 실행
// millisecond 단위 1초=1000
// 두 개의 Thread가 실행되고 난 후
// Thread-0 1~50까지의 합계 출력
// Thread-1 51~100까지의 합계 출력
// Thread-0 + Thread-1의 합계 출력
System.out.println("main thread start");
JoinTest th1 = new JoinTest(1, 50);
JoinTest th2 = new JoinTest(51, 100);
th1.start();
try {
th1.join();
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
th2.start();
try {
th2.join();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
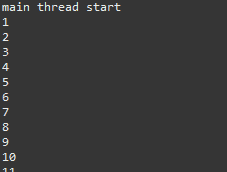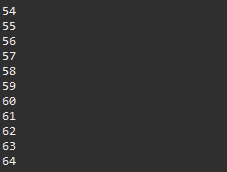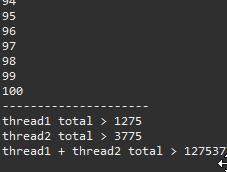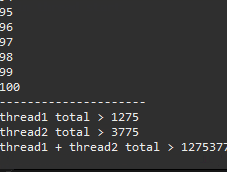
System.out.println("---------------------");
System.out.println("thread1 total > " + th1.total);
System.out.println("thread2 total > " + th2.total);
System.out.println("thread1 + thread2 total > " + th1.total + th2.total);
}
}
▷ 출력
▣ Thread04
package day11;
class Bank{
private int money = 20000;
// 입금 : synchronized : 동기화(순차접근)
public synchronized void saveMoney(int save) {
int m = this.money;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.money = m + save;
}
// 출금
public synchronized void minusMoney(int minus) {
int m = this.money;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.money = m - minus;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
class Hong extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
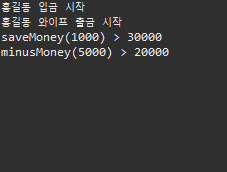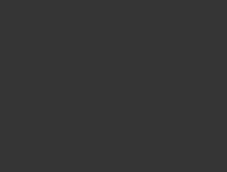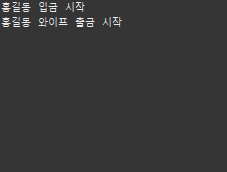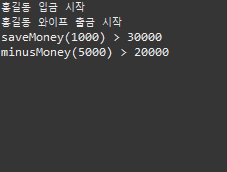
System.out.println("홍길동 입금 시작");
Thread04.myBank.saveMoney(10000);
System.out.println("saveMoney(1000) > " + Thread04.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
class HongWife extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("홍길동 와이프 출금 시작");
Thread04.myBank.minusMoney(10000);
System.out.println("minusMoney(5000) > " + Thread04.myBank.getMoney());
}
}
public class Thread04 {
// 계좌 생성 : 공유영역에 생성
public static Bank myBank = new Bank();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hong h = new Hong();
h.start();
HongWife hw = new HongWife();
hw.start();
/* critical section(임계영역)은 두 개 이상의 thread가
* 동시에 접근할 수 있는 영역 (공유영역)
* 동시에 여러 개의 thread가 접근하여 공유영역을 가지려고하면 문제가 생길 수 있음.
* 교착상태(deadlock)가 발생
* 한 순간에는 하나의 thread만 사용가능 : 세마포어(semaphore)
* 세마포어를 얻은 스레드만 접근이 가능 / 나머지는 대기상태가 됨
*
* 동기화(순서화) : synchronized
* 동기화가 필요한 메서드 앞에 선언
*/
/* bank 클래스 생성
* 계좌 1개 생성 => 공유영역 (static)
* hong / hongwife
* 잔액 : 10000
*/
}
}
▷ 출력
2. Singleton
▣ Network01
package day11;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.URL;
public class Network01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 인터넷 주소의 정보를 확인
InetAddress ip = null;
ip = InetAddress.getByName("www.naver.com");
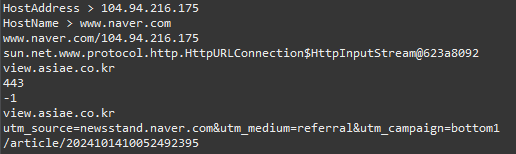
System.out.println("HostAddress > " + ip.getHostAddress());
System.out.println("HostName > " + ip.getHostName());
System.out.println(ip.toString());
URL url = new URL("https://view.asiae.co.kr/article/2024101410052492395?utm_source=newsstand.naver.com&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=bottom1");
System.out.println(url.getContent());
System.out.println(url.getAuthority());
System.out.println(url.getDefaultPort());
System.out.println(url.getPort());
System.out.println(url.getHost());
System.out.println(url.getQuery());
System.out.println(url.getPath());
}
}
▷ 출력
▣ Network02
package day11;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URL;
public class Network02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// http://www.moulian.com/
URL url = null;
String addr = "http://www.moulian.com/";
BufferedReader input = null;
String line = "";
try {
url = new URL(addr);
input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream()));
while((line = input.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
input.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
▷ 출력
(생략)
▣ Singleton01
package day11;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Singleton01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 디자인 패턴 : 개발자들이 개발 과정에서 하나의 패턴으로 묶어놓은 코드 조합
* https://refactoring.guru/ko/design-patterns/what-is-pattern
* 디자인 패턴 중 하나
* 싱글톤 : 단 1개만 존재해야하는 객체를 새엇ㅇ하여 => 공유하고자 할 떄 사용
*/
// Singeton 객체 생성
// Singeton s = new Singeton(); // 생성자가 private라서 생성이 안 됨
// static 메서드 / 멤버변수는 클래스명으로부터 바로 접근
Singeton s = Singeton.getInstance();
Singeton s1 = Singeton.getInstance();
// 하나의 객체를 공유 (주소가 같음)
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s1);
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(c);
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(c1);
}
}
class Singeton{
// 단 1개만 존재하기 위해 객체의 인스턴스 생성 (공유)
private static Singeton instance;
// 생성자를 통해 객체 생성을 막기 위해 생성자를 private 설정
private Singeton() {}
// getInstance() 메서드를 사용하여 instance를 생성 리턴
// instance가 있으면 기존 instance를 리턴
// instance가 없으면 새로 생성해서 리턴
public static Singeton getInstance() {
if(instance == null) {
instance = new Singeton();
}
return instance;
}
}
▷ 출력

▣ Singleton02
package day11;
class Counter{
// 싱글톤으로 생성
private int count;
// 내 객체를 저장하는 멤버변수 (static)
private static Counter instance;
// 생성자 private
private Counter() {}
// 인스턴스를 1개만 생성해주는 메서드
public static Counter getInstance() {
if(instance == null) {
instance = new Counter();
}
return instance;
}
// count가 하나 올라가는 메서드 생성 countMethod()
public int countMethod() {
count++;
return this.count;
}
}
public class Singleton02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Counter 객체를 2개 생성하여 각각 countMethod() 호출
// 1개의 객체가 공유되기 때문에 1개의 변수만 변화
Counter c1 = Counter.getInstance();
Counter c2 = Counter.getInstance();
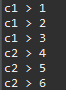
System.out.println("c1 > " + c1.countMethod());
System.out.println("c1 > " + c1.countMethod());
System.out.println("c1 > " + c1.countMethod());
System.out.println("c2 > " + c2.countMethod());
System.out.println("c2 > " + c2.countMethod());
System.out.println("c2 > " + c2.countMethod());
}
}
▷ 출력
3. DB 연결
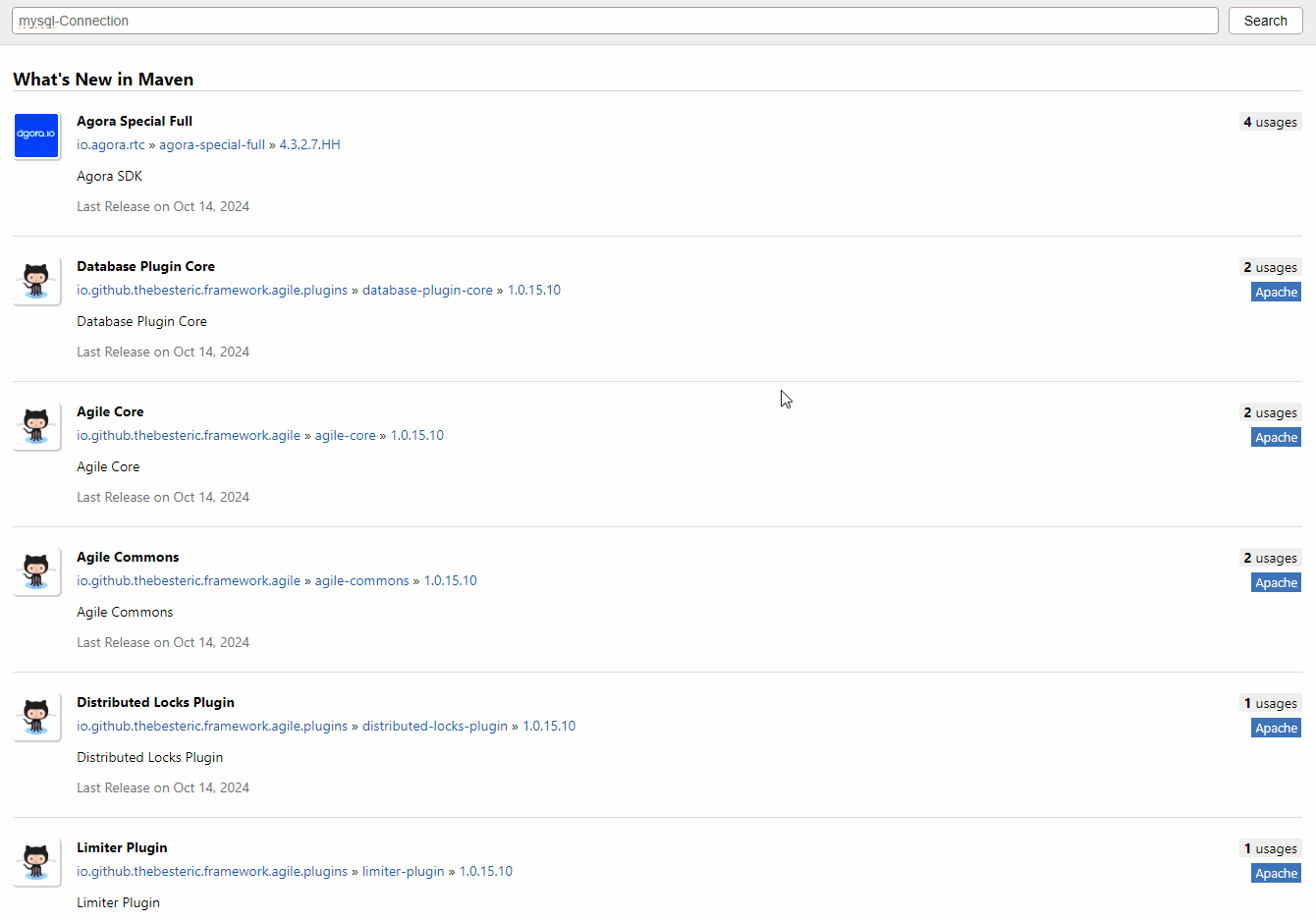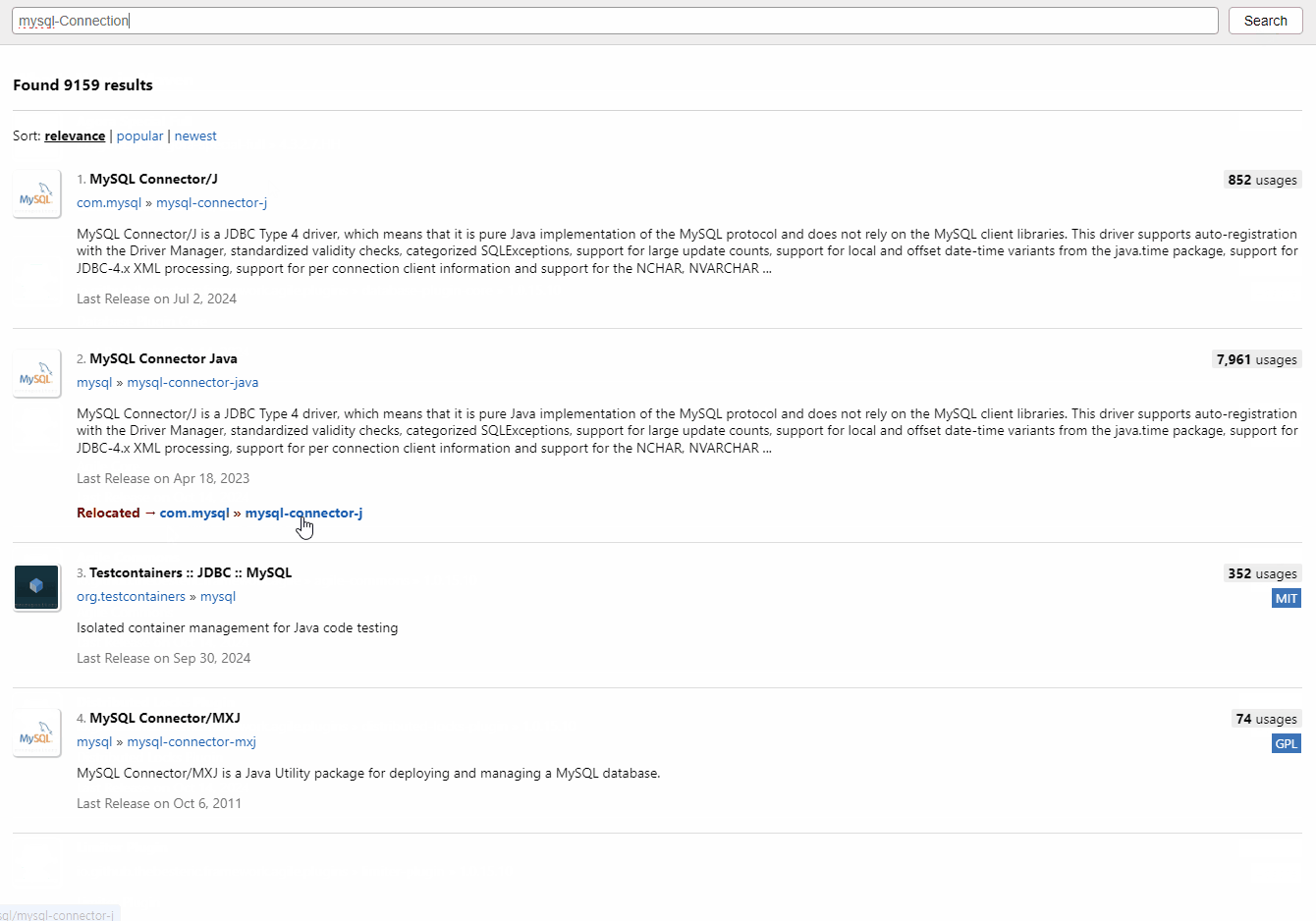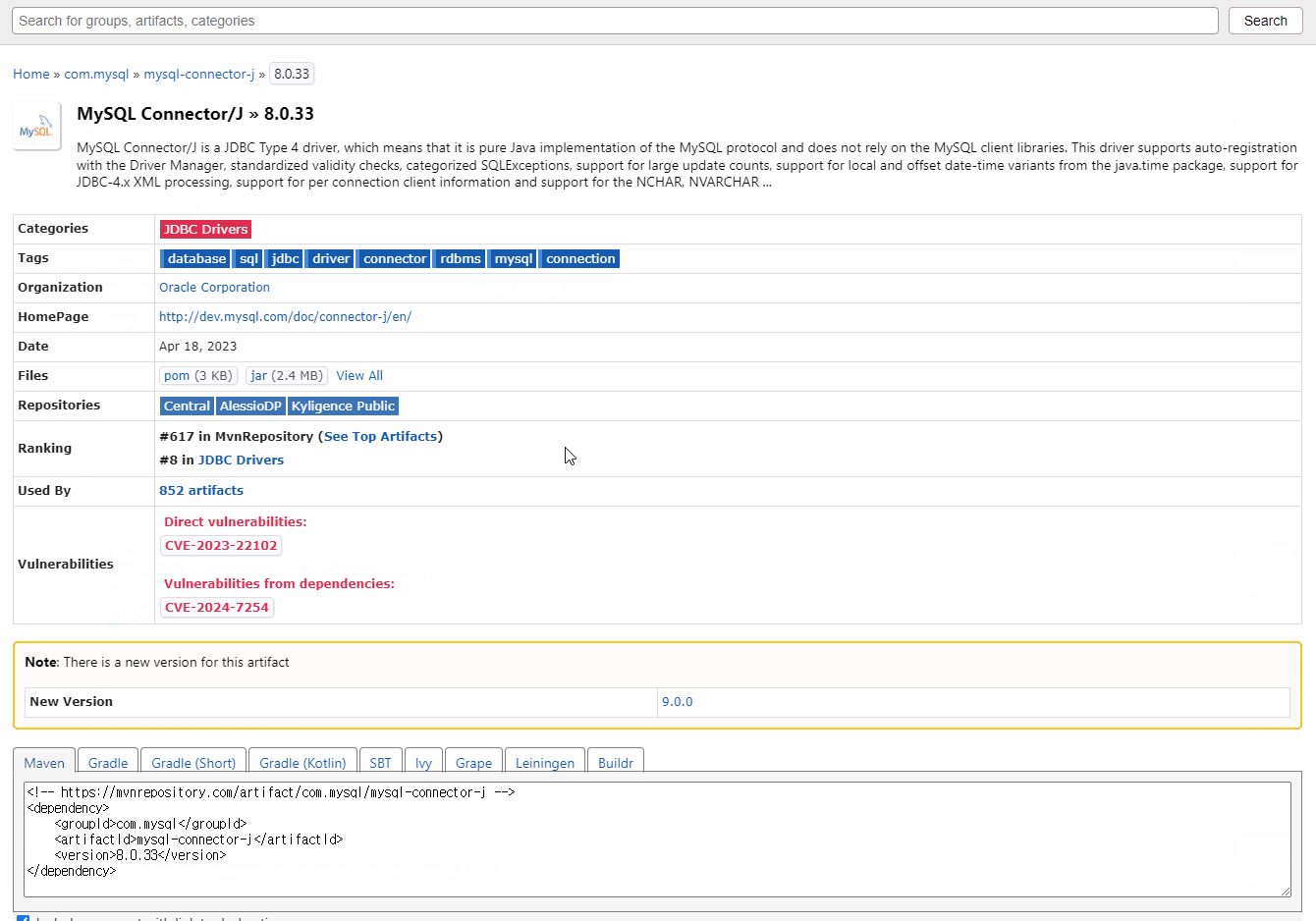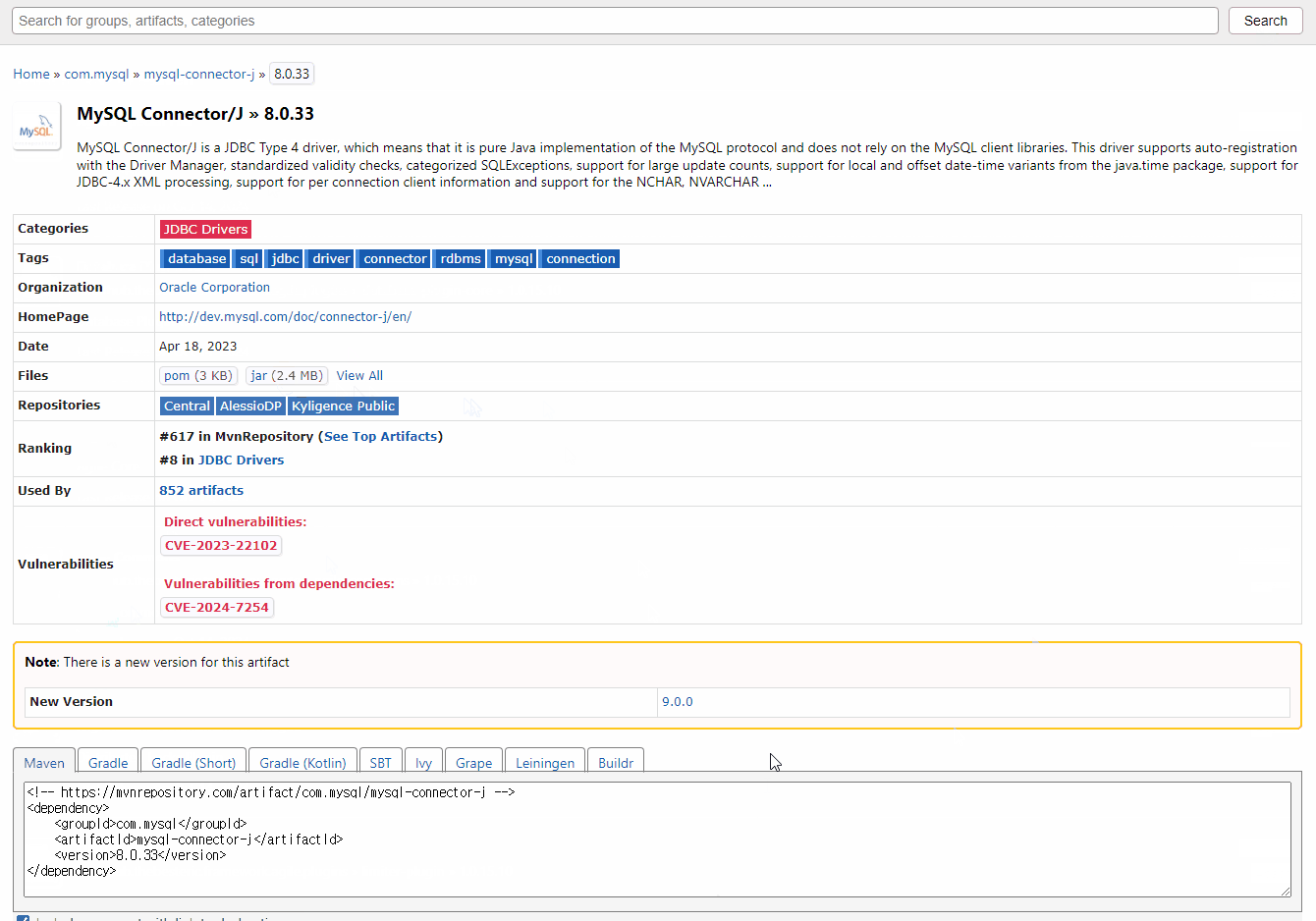
■ 라이브러리 다운로드
- mvnrepository에서 다운로드
(JDBC 필요 - mysql용 8.0.39버전 => 버전은 Workbench에서 왼쪽 하단의 Session에서 확인 가능)
■ DB 테이블 생성 및 권한 부여 (cmd or Workbench)
DB 생성 -> 유저 생성 -> 테이블 생성
상품 정보를 담을 수 있는 DB 생성
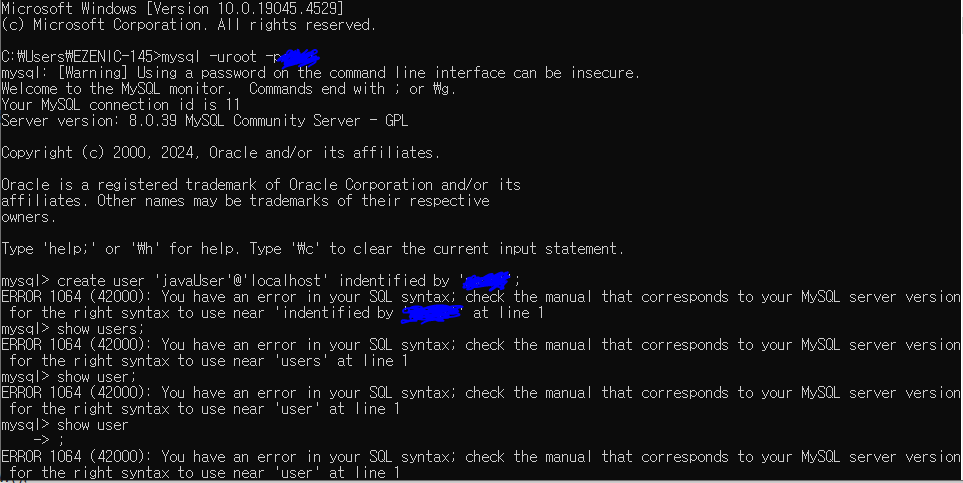
mysql -uroot -p비번
유저 : javaUser
create user 'javaUser'@'localhost' identified by '비번';
DB : javadb
create database javadb;
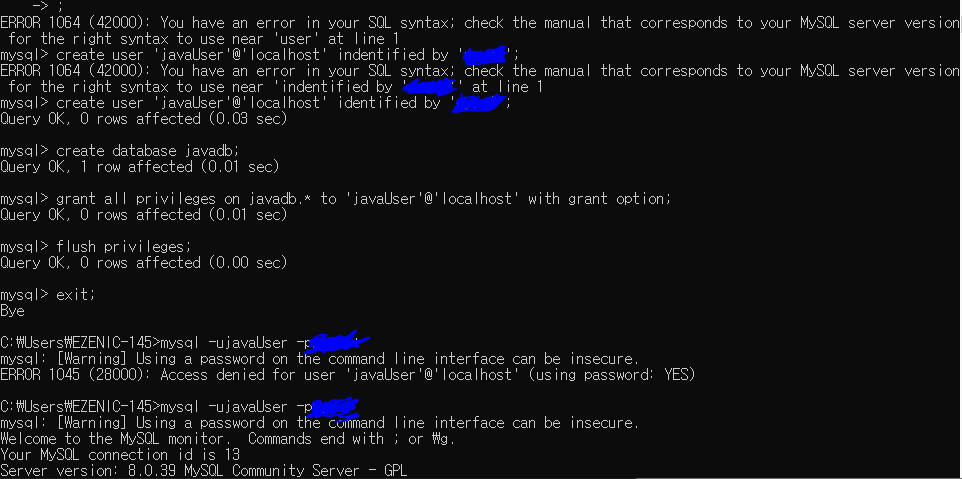
권한 부여
grant all privileges on javadb.* to 'javaUser'@'localhost' with grant option;
flush privileges;
exit;
mysql -ujavaUser -p비번
use javadb
테이블 : product
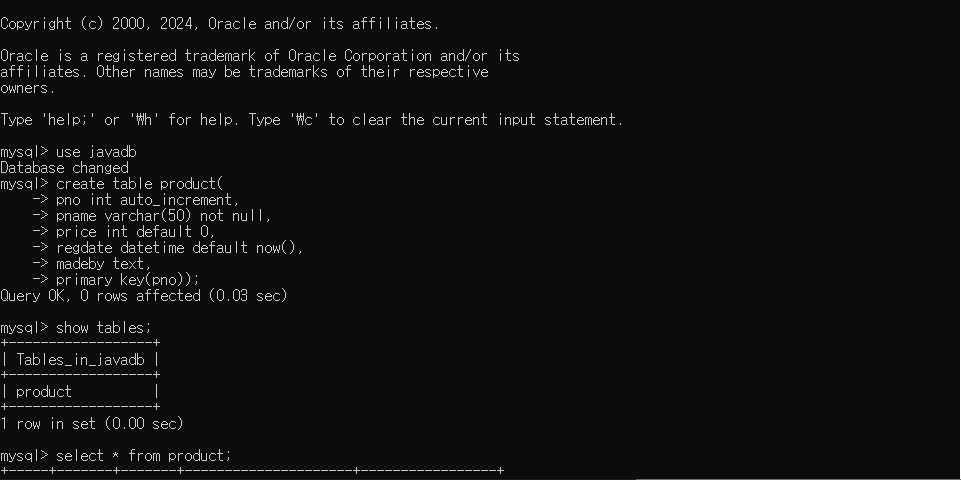
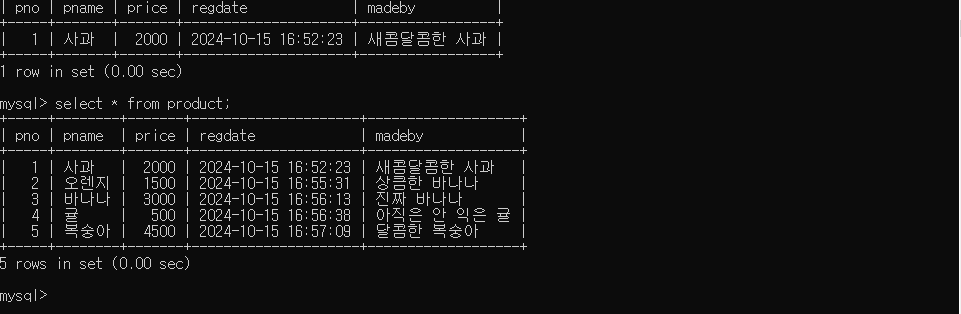
create table product(
pno int auto_increment,
pname varchar(50) not null,
price int default 0,
regdate datetime default now(),
madeby text,
primary key(pno));
■ eclipse 라이브러리 추가
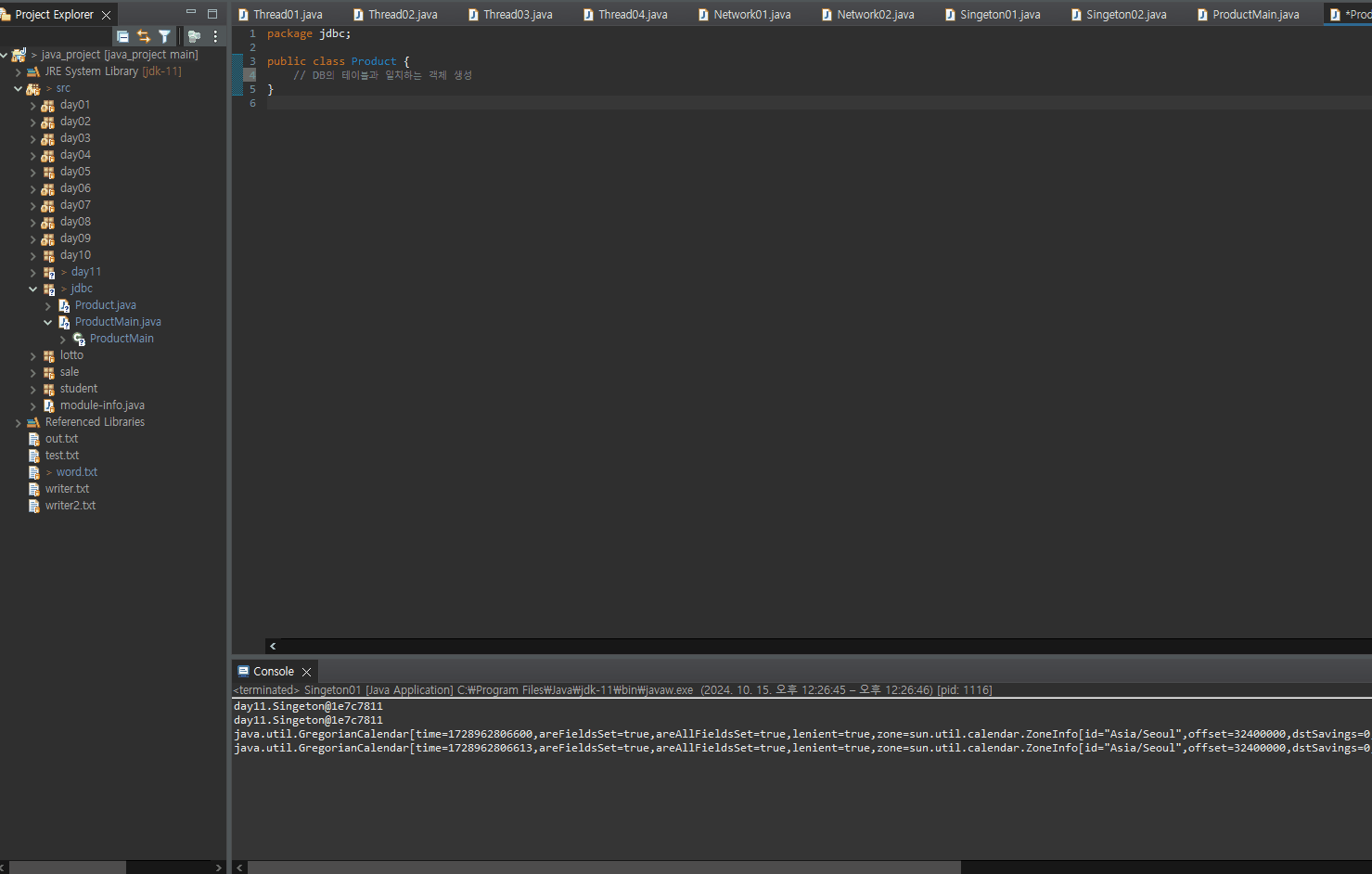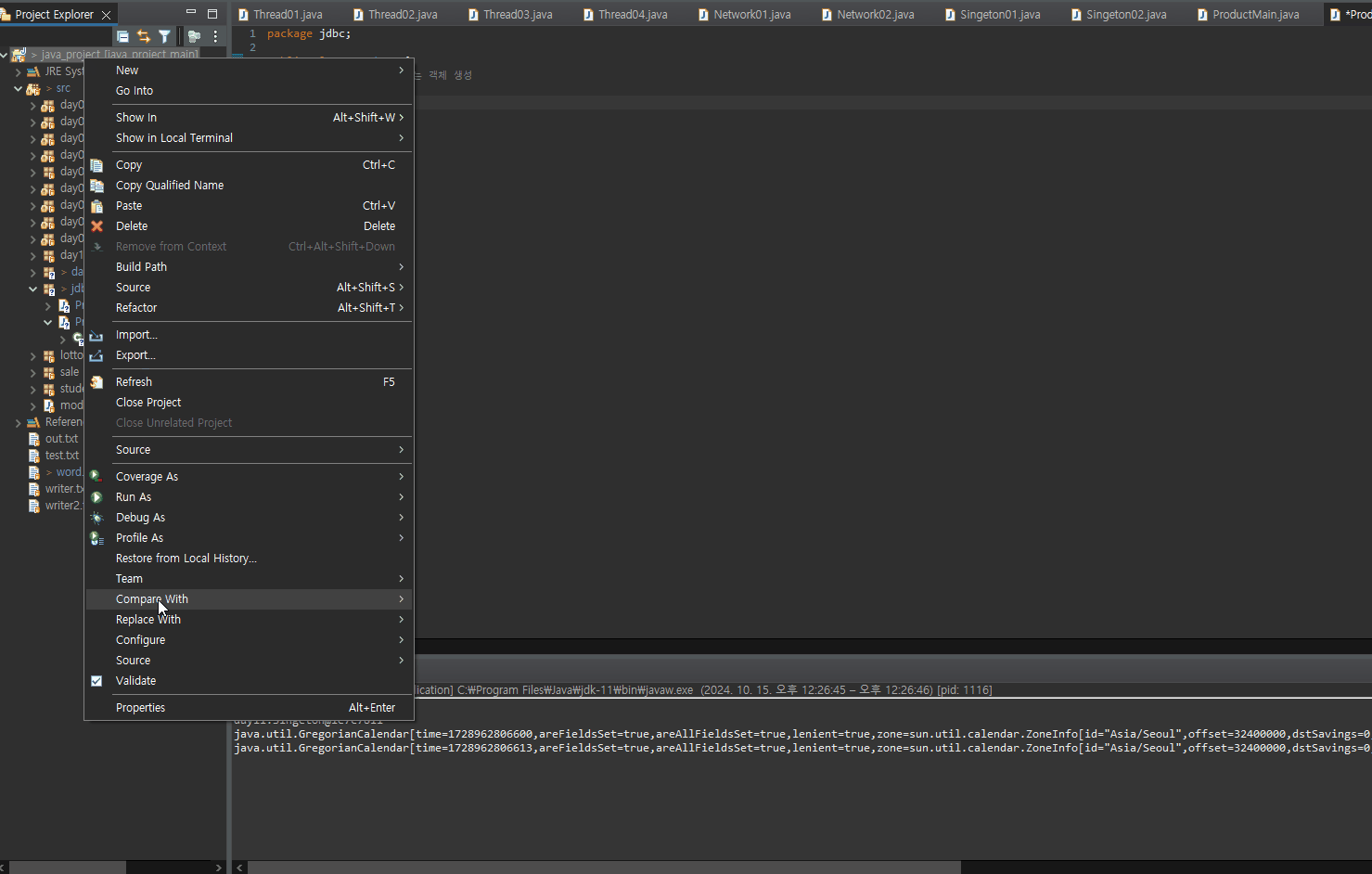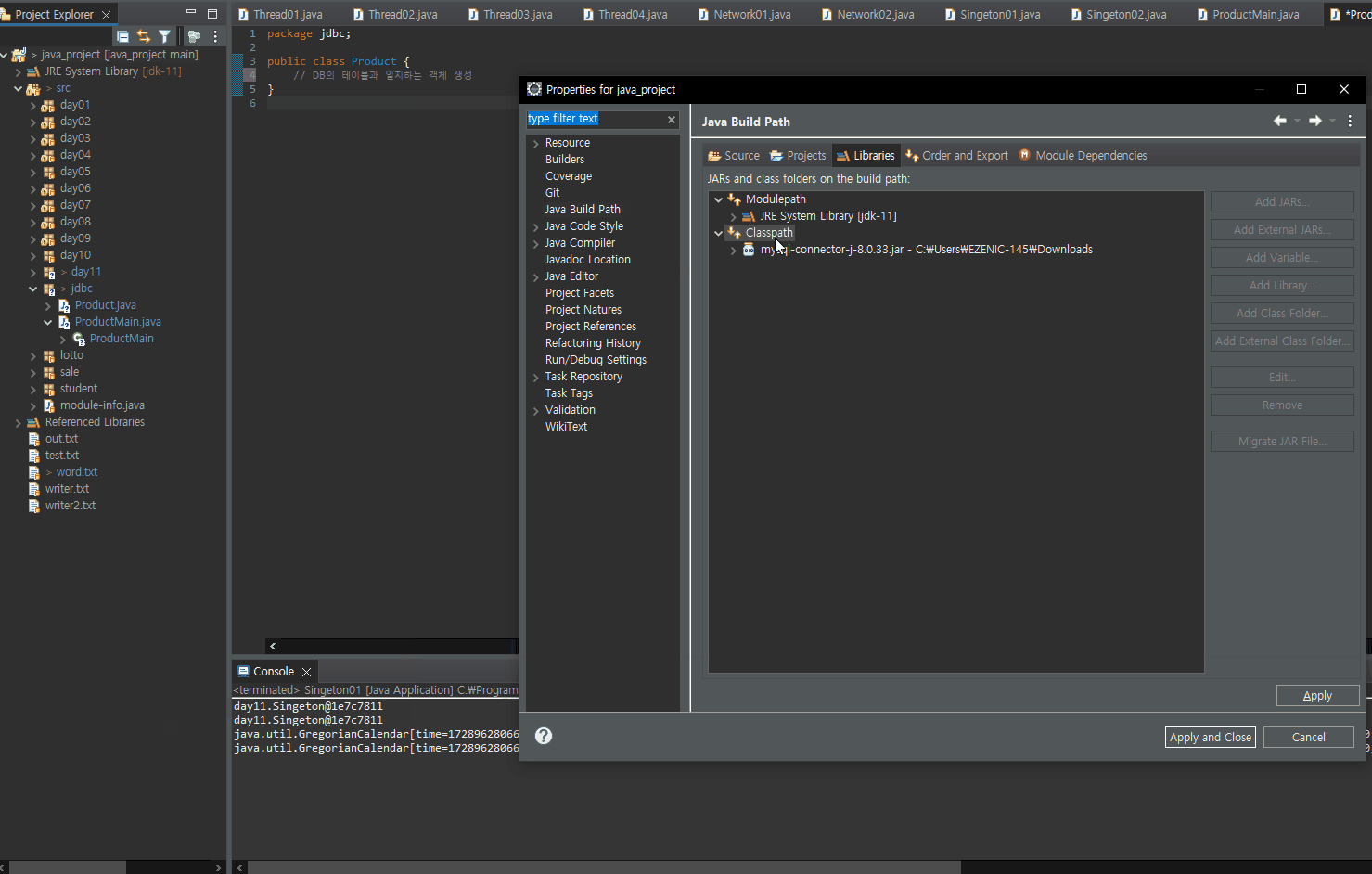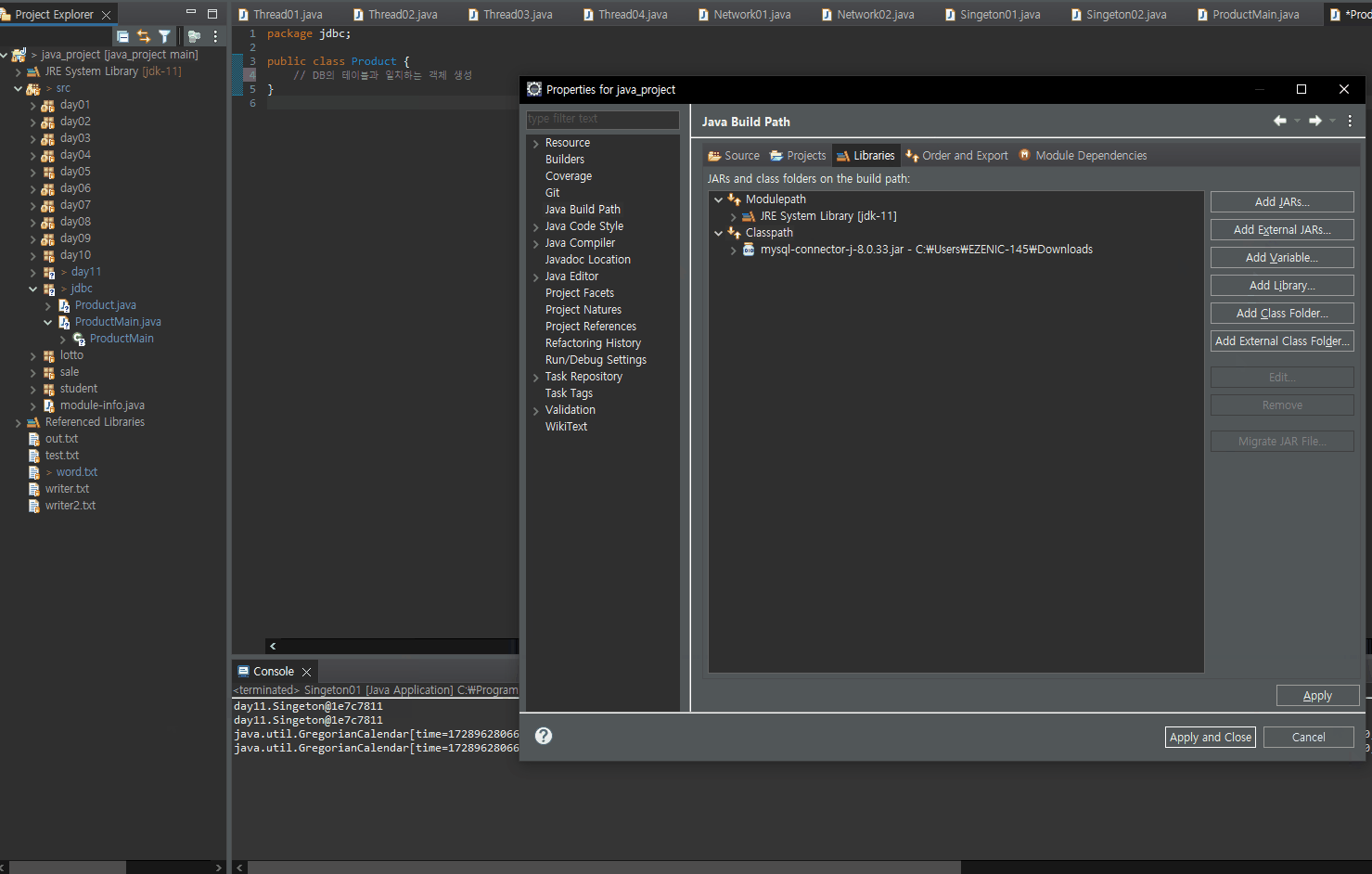
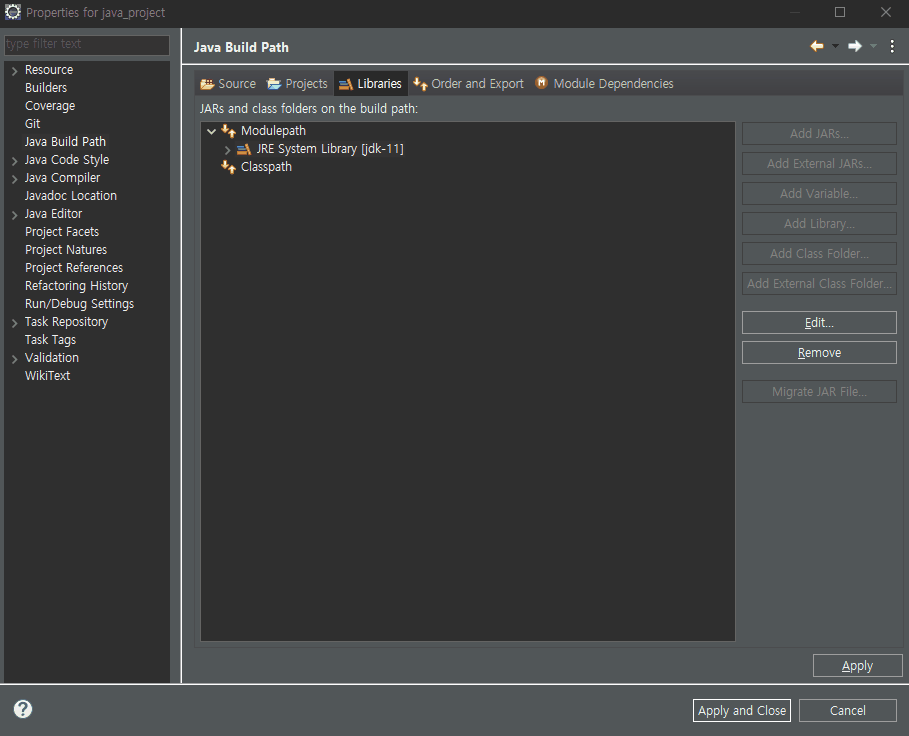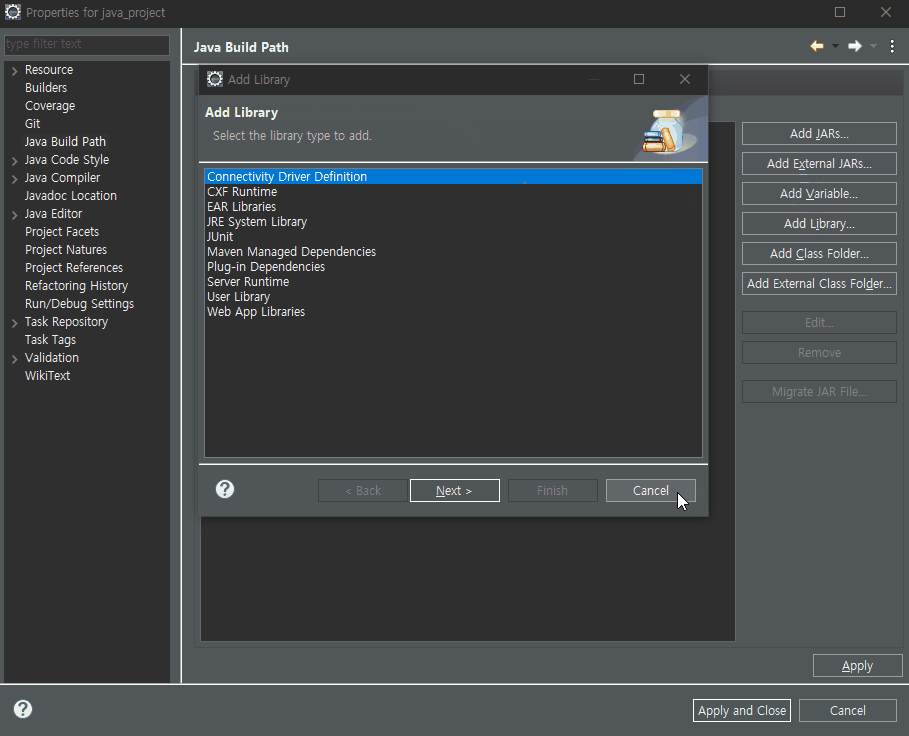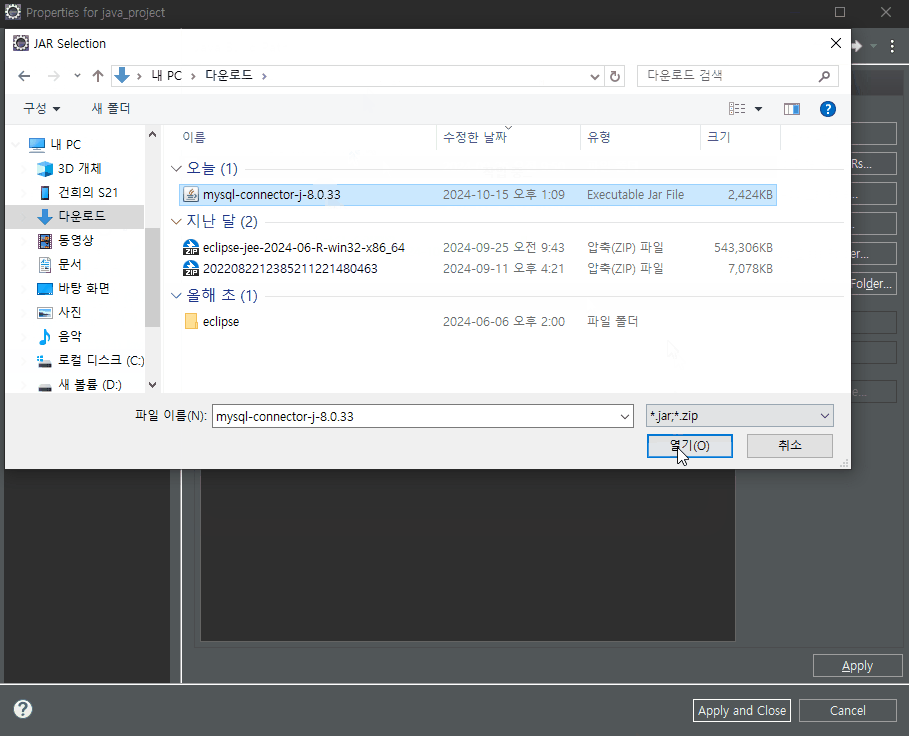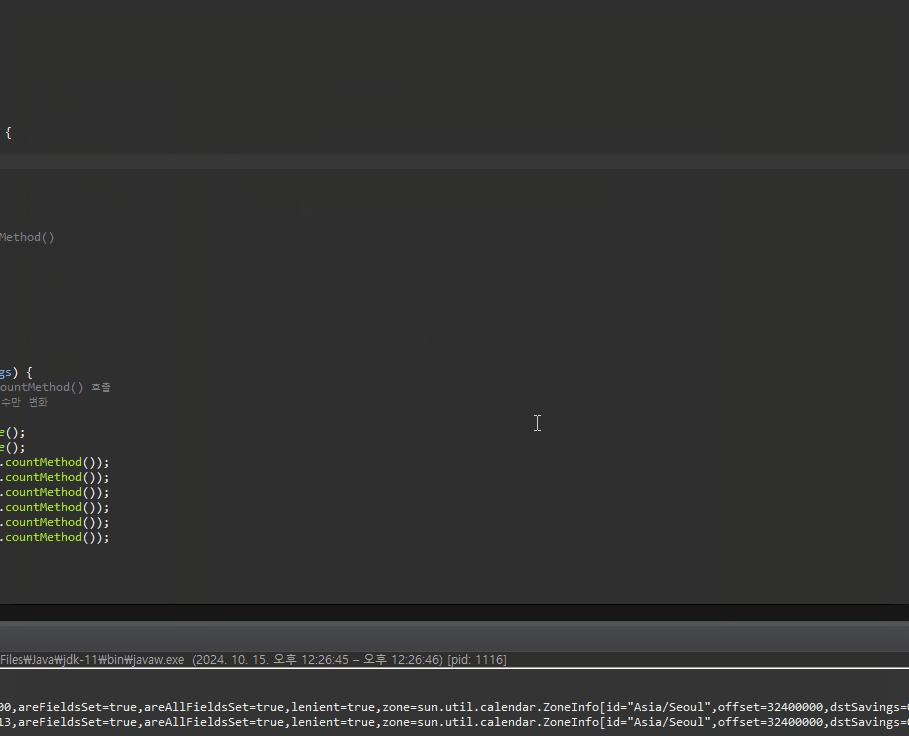
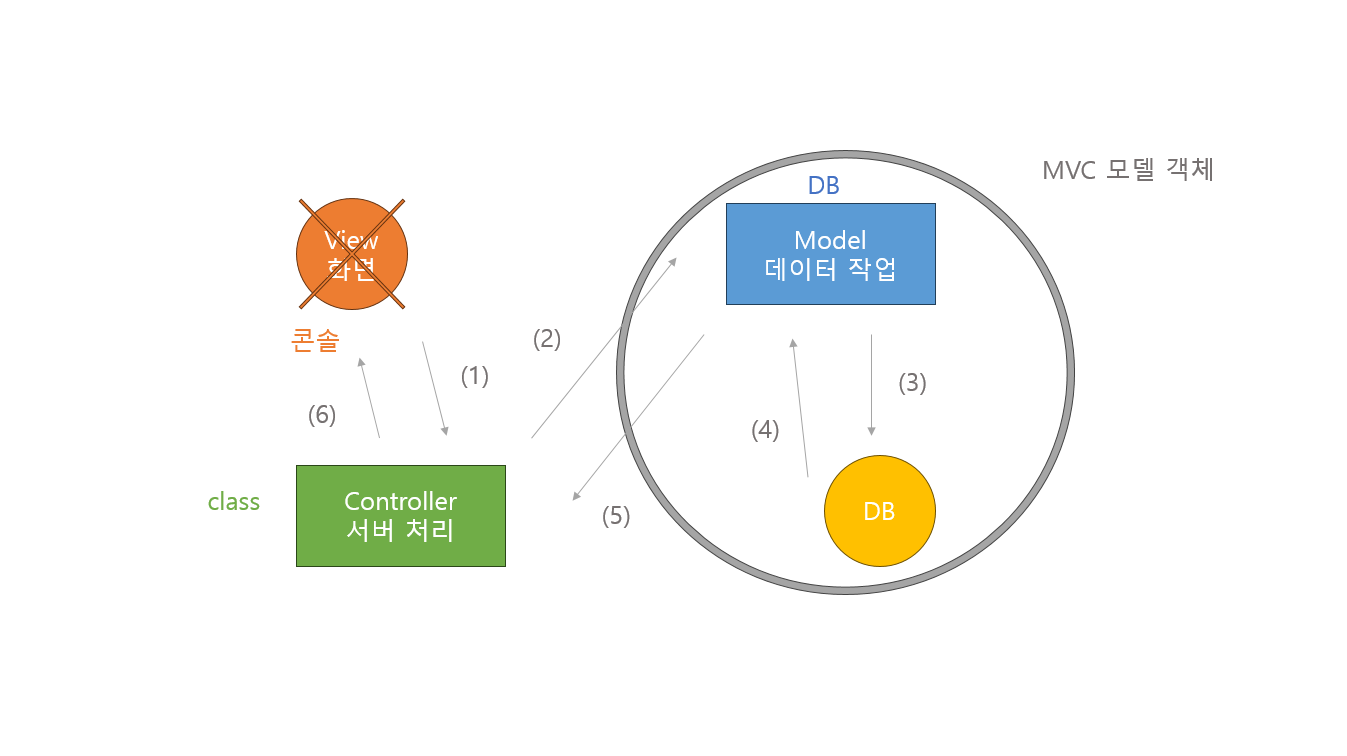
■ 이론
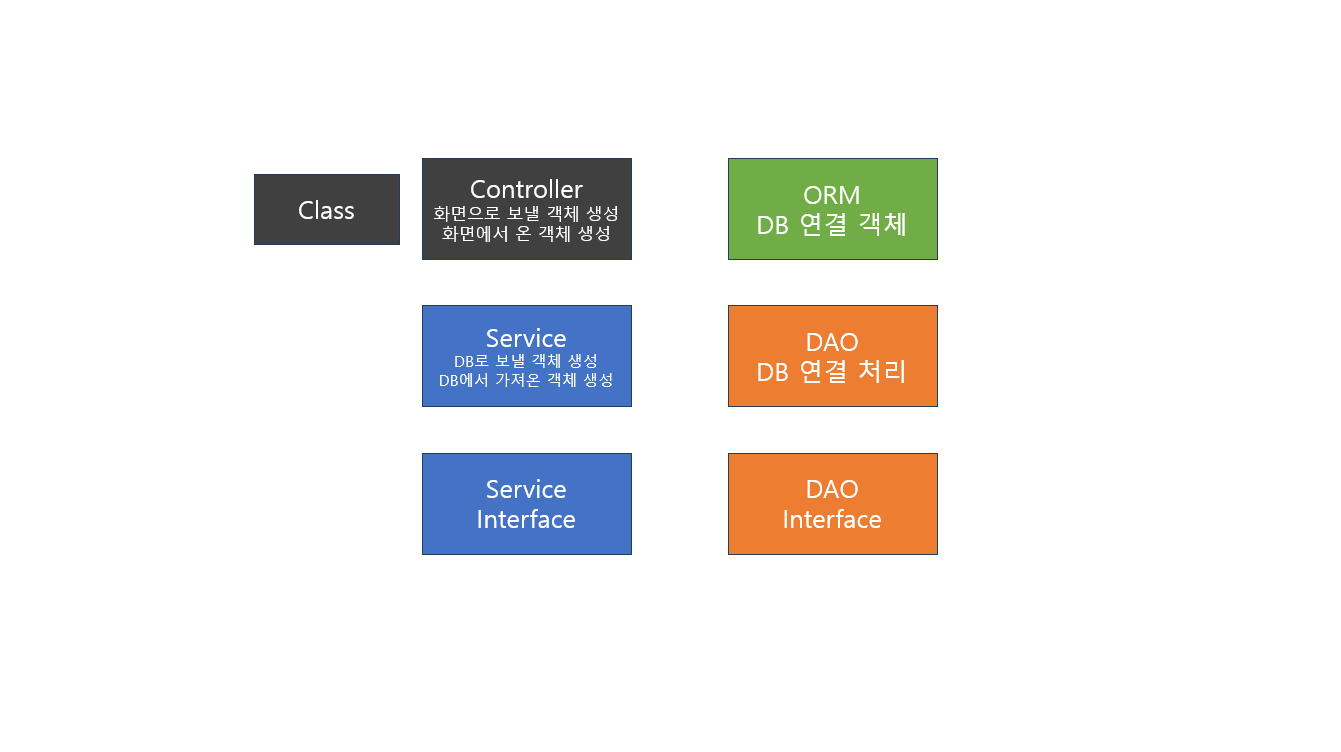
▣ ProductMain
package jdbc;
public class ProductMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ProductController();
}
}
▣ Product
package jdbc;
public class Product {
// DB의 테이블과 일치하는 객체 생성
// pno int auto_increment,
// pname varchar(50) not null,
// price int default 0,
// regdate datetime default now(),
// madeby text,
private int pno; // 자동 생성
private String pname;
private int price;
private String regdate; // now()
private String madeby;
// 생성자 / getter setter / toString
public Product() {}
// 상품등록 -> pname, price, madeby
public Product(String pname, int price, String madeby) {
this.pname = pname;
this.price = price;
this.madeby = madeby;
}
// 상품리스트 -> pno, pname, price
public Product(int pno, String pname, int price) {
this.pno = pno;
this.pname = pname;
this.price = price;
}
// 상품상세보기 -> 전부
public Product(int pno, String pname, int price, String regdate, String madeby) {
this.pno = pno;
this.pname = pname;
this.price = price;
this.regdate = regdate;
this.madeby = madeby;
}
// 상품수정 -> pname, price, madeby, pno
public Product(String pname, int price, String madeby, int pno) {
this.pname = pname;
this.price = price;
this.madeby = madeby;
this.pno = pno;
}
public int getPno() {
return pno;
}
public void setPno(int pno) {
this.pno = pno;
}
public String getPname() {
return pname;
}
public void setPname(String pname) {
this.pname = pname;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getRegdate() {
return regdate;
}
public void setRegdate(String regdate) {
this.regdate = regdate;
}
public String getMadeby() {
return madeby;
}
public void setMadeby(String madeby) {
this.madeby = madeby;
}
public String print() {
return pno + ". " + pname + "(" + price + ")";
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return pno + ". " + pname + "(" + price + ") / " + regdate + "["
+ madeby + "]";
}
}
▣ sqlFile
-- 기록용 나중에 유저와 비번 db를 확인한 목적
create user 'javaUser'@'localhost' identified by 'mysql';
create database javadb;
grant all privileges on javadb.* to 'javaUser'@'localhost' with grant option;
flush privileges;
exit;
mysql -ujavaUser -pmysql
use javadb
create table product(
pno int auto_increment,
pname varchar(50) not null,
price int default 0,
regdate datetime default now(),
madeby text,
primary key(pno));
-- db는 수정되거나 추가되면 변경 구문을 써놓아야함
▣ ProductController
package jdbc;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ProductController {
/* Controller <-> Service <-> DAO <-> DB
* Controller 모든 메뉴 분기 처리
*/
private Scanner scan;
private Service svc; // 아직 없음 interface
private boolean flag;
public ProductController() {
scan = new Scanner(System.in);
svc = new ProductServiceImpl(); // service interface 구현체
flag = true;
printMenu();
}
private void printMenu() {
while(flag) {
System.out.println("--상품관리프로그램--");
System.out.println("1.상품등록|2.상품목록|3.상품검색(상세보기)|4.상품수정|5.상품삭제|6.종료");
System.out.println("menu > ");
int menu = scan.nextInt();
switch(menu) {
case 1: register(); break;
case 2: list(); break;
case 3: search(); break;
case 4: modify(); break;
case 5: delete(); break;
case 6:
flag = false;
System.out.println("종료");
break;
default: System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴");
}
}
}
private void delete() {
// 상품 삭제
// 삭제할 번호(pno) isOk return
System.out.println("검색할 번호 입력:");
int pno = scan.nextInt();
// 메서드 명은 상관없음. (기능과 관련있게 명명)
// set get insert register add update modify remove delete
int isOk = svc.delete(pno);
System.out.println("상품삭제 > " +(isOk > 0 ? "성공" : "실패"));
}
private void modify() {
// 상품 수정 : 이름, 가격, 상세내용
System.out.println("검색할 번호 입력:");
int pno = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("상품이름:");
String name = scan.next();
System.out.println("상품가격:");
int price = scan.nextInt();
scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("상품상세내역:");
String madeby = scan.nextLine(); // 공백포함
Product p = new Product(name, price, madeby, pno);
int isOk = svc.update(p);
System.out.println("상품등록 > " +(isOk > 0 ? "성공" : "실패"));
}
private void search() {
// 특정 상품 검색(세부 내용 madeby / regdate)
// pno가 필요
// select * from product where pno = ?
// pno 값을 입력받아 매개변수로 전달 Product 객체 리턴
System.out.println("검색할 번호 입력:");
int pno = scan.nextInt();
Product p = svc.getProduct(pno);
System.out.println(p);
}
private void list() {
// 상품 전체 리스트
// 매개변수는 없고, 리턴 List
// select * from product order by pno desc
List<Product> list = svc.getList();
// 출력
for(Product p : list) {
System.out.println(p.print());
}
}
private void register() {
// 상품등록
System.out.println("상품이름:");
String name = scan.next();
System.out.println("상품가격:");
int price = scan.nextInt();
scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("상품상세내역:");
String madeby = scan.nextLine(); // 공백포함
Product p = new Product(name, price, madeby);
// service에게 p 객체 등록 요청 (메서드 작성)
// 1 row(s) affected 0.016 sec
// isOk = 1 (DB에 성공적으로 들어감) / isOk = 0 (실패)
int isOk = svc.insert(p);
System.out.println("상품등록 > " +(isOk > 0 ? "성공" : "실패"));
}
}
▣ Service
package jdbc;
import java.util.List;
public interface Service {
int insert(Product p);
List<Product> getList();
Product getProduct(int pno);
int update(Product p);
int delete(int pno);
}
▣ ProductService
package jdbc;
import java.util.List;
public class ProductServiceImpl implements Service {
/* service <-> DAO */
// 생성자로 DAO 객체와 연결
private DAO dao; // interface
public ProductServiceImpl() {
dao = new ProductDAOImpl(); // DAO 구현체
}
@Override
public int insert(Product p) {
// 실제 구현 영역
System.out.println("상품등록 serviceImpl Success");
// DAO에게 DB 저장을 요청
// dao 요청시 메서드명은 sql구문과 비슷하게 작성하는 것이 일반적
return dao.insert(p);
}
@Override
public List<Product> getList() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("list serviceImpl Success");
return dao.selectList();
}
@Override
public Product getProduct(int pno) {
System.out.println("product serviceImpl Success");
return dao.selectProduct(pno);
}
@Override
public int update(Product p) {
System.out.println("update serviceImpl Success");
return dao.update(p);
}
@Override
public int delete(int pno) {
System.out.println("delete serviceImpl Success");
return dao.delete(pno);
}
}
▣ DAO
package jdbc;
import java.util.List;
public interface DAO {
int insert(Product p);
List<Product> selectList();
Product selectProduct(int pno);
int update(Product p);
int delete(int pno);
}
▣ ProductDAOImpl
package jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ProductDAOImpl implements DAO {
/* DAO <-> DB
*/
// DB 연결객체
private Connection conn;
// sql 구문을 실행시키는 기능을 가진 객체
private PreparedStatement pst;
// 쿼리문 저장 스트링
private String query = "";
public ProductDAOImpl() {
// DBConnection class 생성(싱글톤) 연걸
DatabaseConnection dbc = DatabaseConnection.getInstance();
conn = dbc.getConnection();
}
// sql 처리
@Override
public int insert(Product p) {
// product 객체를 등록하고, isOk를 리턴
System.out.println("insert DAOImpl success");
query = "insert into product(pname, price, madeby) values(?, ?, ?)";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(query);
// ? 반드시 순서대로 처리 (자료형을 기재) 1부터 시작
pst.setString(1, p.getPname());
pst.setInt(2, p.getPrice());
pst.setString(3, p.getMadeby());
// insert, update, delete => 처리만... (1 row(s) affected)
// 결과의 행 수만 리턴 => executeUpdate(); int 리턴
// select => 목록 => executeQuery(); ResultSet으로 리턴
return pst.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// insert error
System.out.println("insert error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public List<Product> selectList() {
// DB에서 리스트를 가져와서 리턴
System.out.println("list DAOImpl success!!");
query = "select * from product order by pno desc";
List<Product> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(query);
// select => 목록 => executeQuery(); ResultSet으로 리턴
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();
// ResultSet => List로 변환 (pno, pname, price)
while(rs.next()) {
list.add(new Product(rs.getInt("pno"), rs.getString("pname"), rs.getInt("price")));
}
return list;
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("list error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Product selectProduct(int pno) {
System.out.println("product DAOImpl success!!");
query = "select * from product where pno = ?";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pst.setInt(1, pno);
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()) {
Product p = new Product(rs.getInt("pno"), rs.getString("pname"), rs.getInt("price"), rs.getString("regdate"), rs.getString("madeby"));
return p;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("product error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public int update(Product p) {
System.out.println("update DAOImpl success!!");
query = "update product set pname = ?, price = ?, madeby = ?, regdate = now() where pno = ?";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pst.setString(1, p.getPname());
pst.setInt(2, p.getPrice());
pst.setString(3, p.getMadeby());
pst.setInt(4, p.getPno());
return pst.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("update error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public int delete(int pno) {
System.out.println("delete DAOImpl success!!");
query = "delete from product where pno = ?";
try {
pst = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pst.setInt(1, pno);
return pst.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("delete error");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 0;
}
}
▣ DatabaseConnection
package jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DatabaseConnection {
/* DB 접속 객체
* DB Driver, url, user, password
* com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
* jdbc:myㄴql://localhost:3306/DB명
*/
private static DatabaseConnection dbc = new DatabaseConnection();
private Connection conn = null;
private String jdbDriver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private String jdbUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/javadb";
// 생성자
private DatabaseConnection() {
try {
// 드라이버를 로드하기 위한 메서드
Class.forName(jdbDriver);
// 연결을 위해서 url, user, password
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbUrl, "javaUser", "mysql");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// 드라이버를 찾을 수 없을 경우
System.out.println("드라이버를 찾을 수 없습니다");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// con 연결정보가 잘못되었을 경우
System.out.println("연결정보가 정확하지 않습니다.");
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static DatabaseConnection getInstance() {
return dbc;
}
public Connection getConnection() {
return conn;
}
}
▷ 출력

'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java 기초(실습)- AWS 풀스택 과정 57일차 (0) | 2024.10.16 |
|---|---|
| Java 기초(File)- AWS 풀스택 과정 55일차 (0) | 2024.10.14 |
| Java 기초(Generics, lambda)- AWS 풀스택 과정 54일차 (0) | 2024.10.11 |
| Java 기초(map)- AWS 풀스택 과정 53일차 (4) | 2024.10.10 |
| Java 기초(polymorphism)- AWS 풀스택 과정 52일차 (10) | 2024.10.08 |