오늘은 ERD에 대해서 배워보겠습니다.
| 목차 | |
| 1. | DML |
| 2. | ERD |
| 3. | 예제 문제 |
| 4. | 느낀 점 |
1. DML
DB - day03
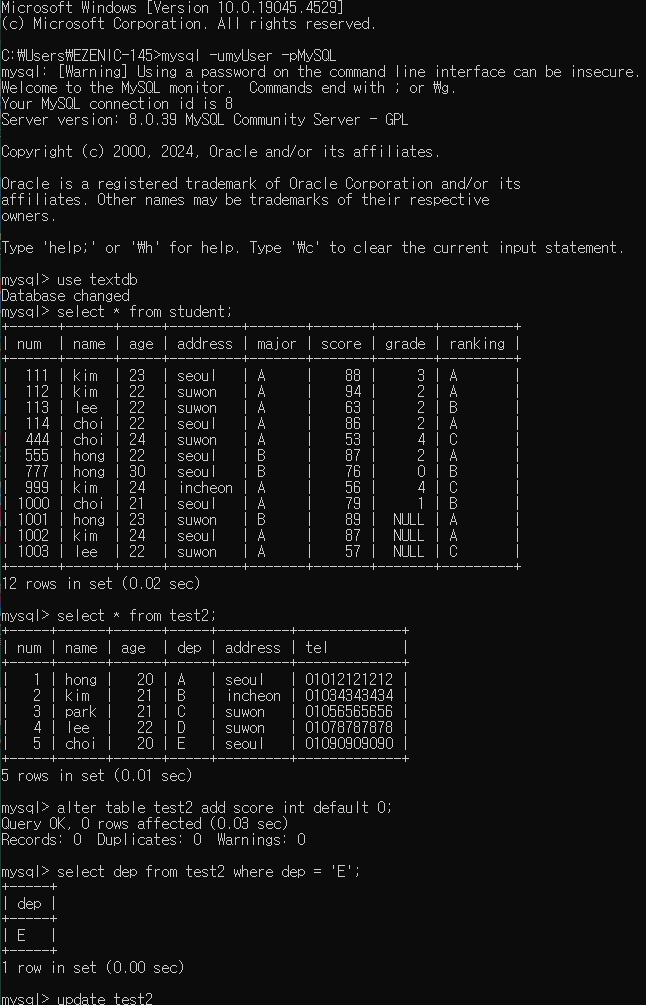
test2 테이블에서 확인
1. score 칼럼 추가 기본값으로 0으로 설정
alter table test2 add score int default 0;
2. 학과가 E인 학생들을 출력
select dep from test2 where dep = 'E';
3. 학과가 E인 튜플을 A로 변경
update test2
set dep = 'A'
where dep = 'E';
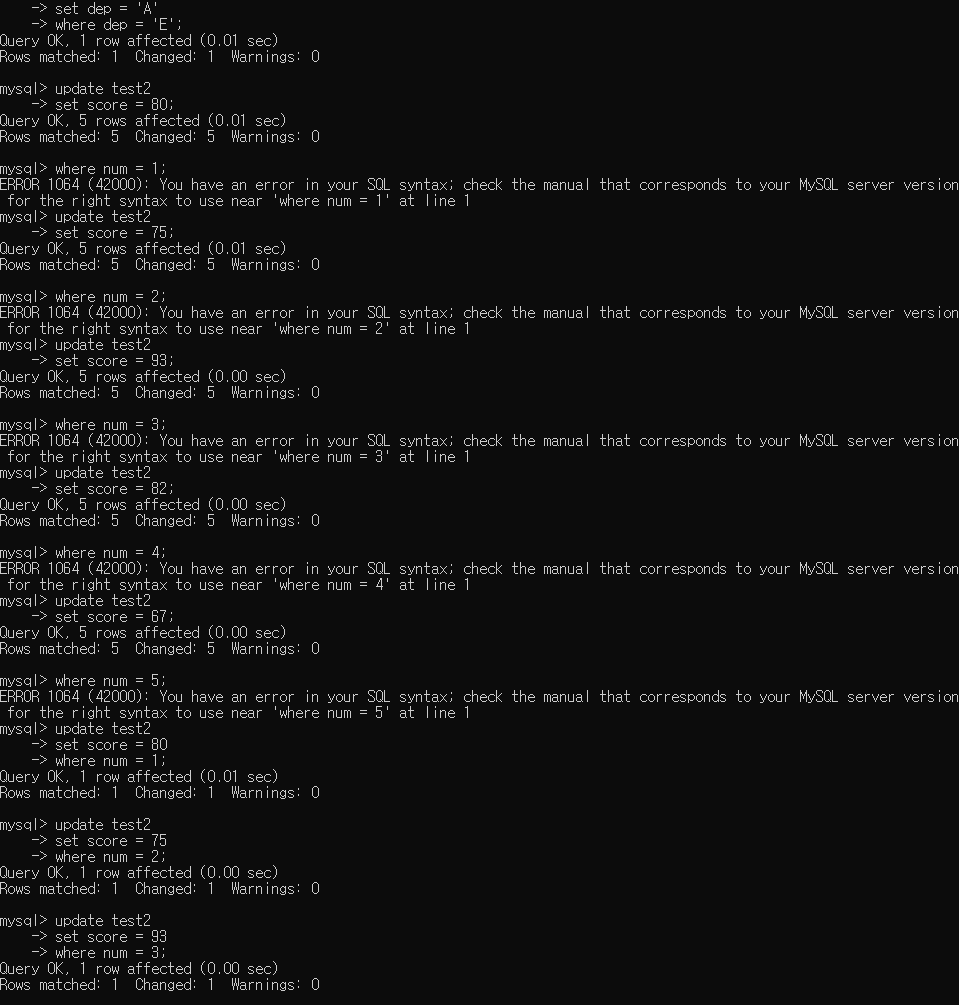
4. score의 값을 update
update test2
set score = 80
where num = 1;
update test2
set score = 75
where num = 2;
update test2
set score = 93
where num = 3;
update test2
set score = 82
where num = 4;
update test2
set score = 67
where num = 5;
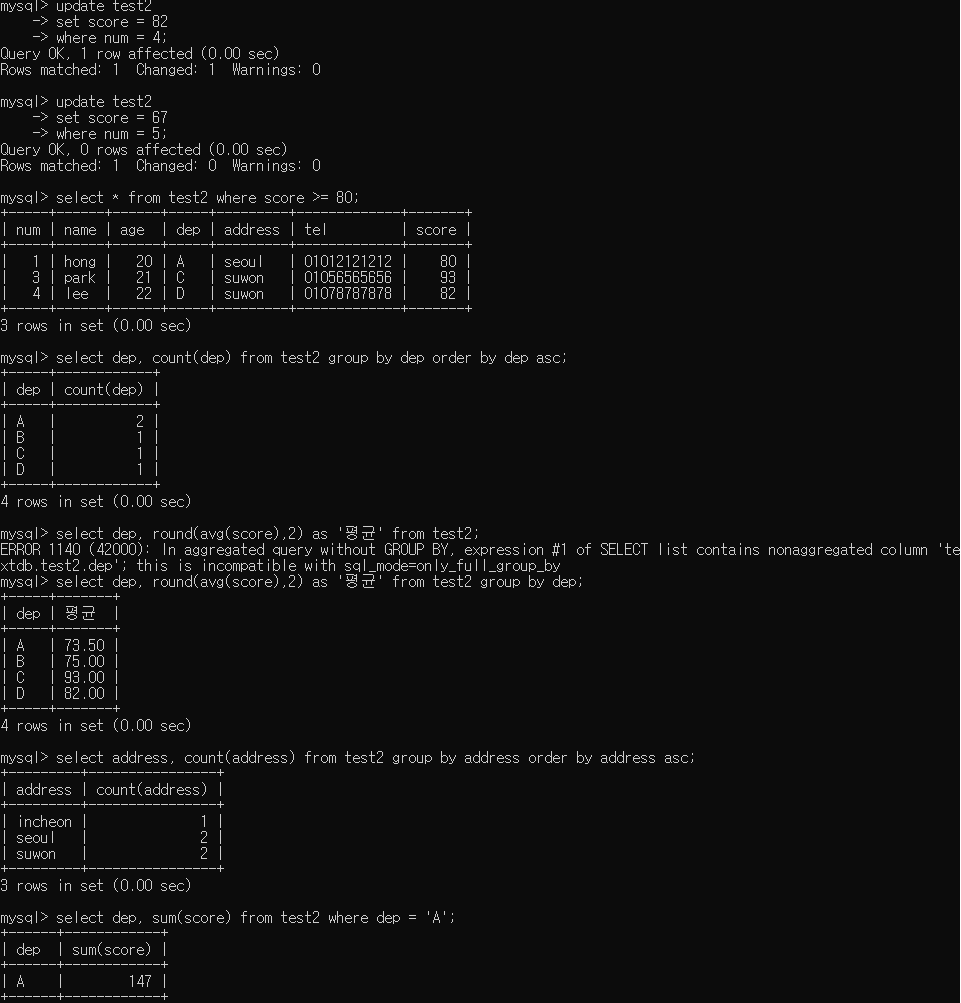
5. score가 80 이상인 학생들만 출력
select * from test2 where score >= 80;
6. 학과별 인원수 출력 (학과별로 오름차순)
select dep, count(dep) from test2 group by dep order by dep asc;
7. 학과별 성적 평균 (소수점 2자리 반올림) 칼럼명 평균
select dep, round(avg(score),2) as '평균' from test2 group by dep;
8. 주소별 인원수 출력 (주소별로 오름차순)
select address, count(address) from test2 group by address order by address asc;
9. A학과만 성적 합계 출력
select dep, sum(score) from test2 where dep = 'A';
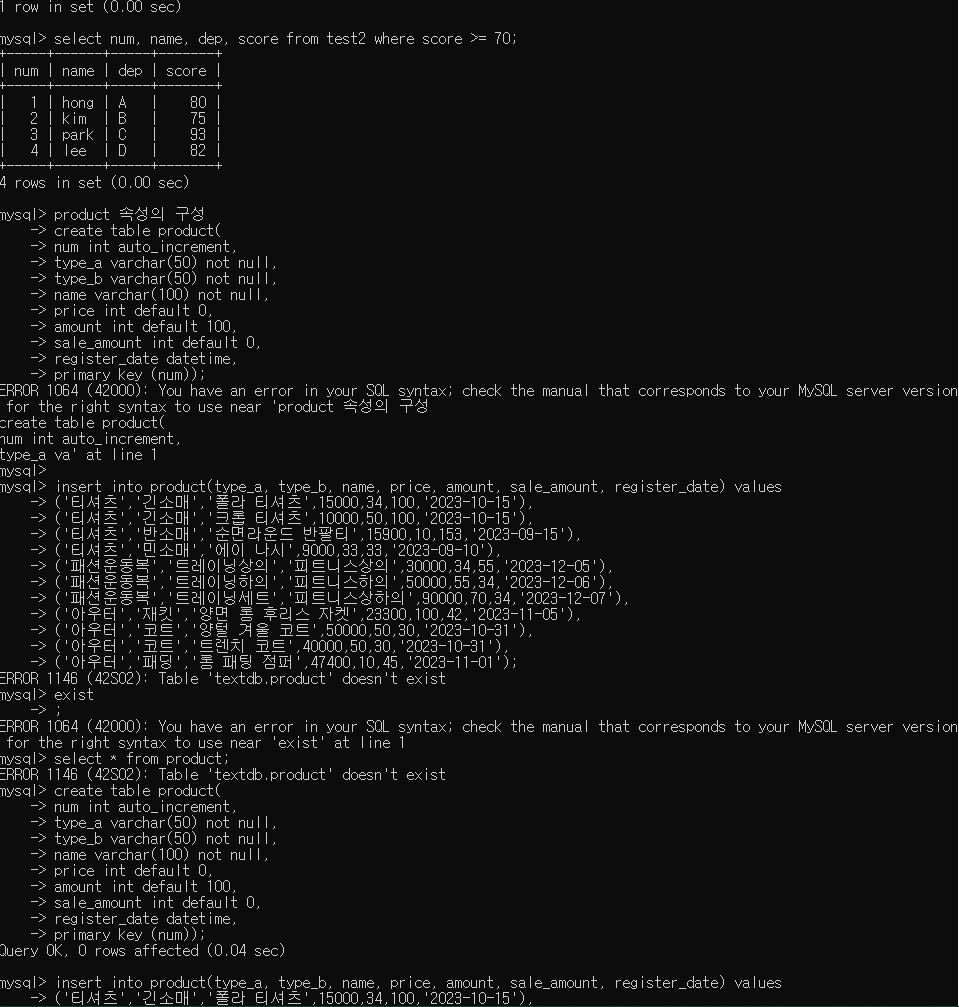
10. 성적이 70점 이상인 학생들의 num, name, dep, score만 출력
select num, name, dep, score from test2 where score >= 70;
----------------------------------------------------
- 제품 테이블(product)
product 속성의 구성
create table product(
num int auto_increment,
type_a varchar(50) not null,
type_b varchar(50) not null,
name varchar(100) not null,
price int default 0,
amount int default 100,
sale_amount int default 0,
register_date datetime,
primary key (num));
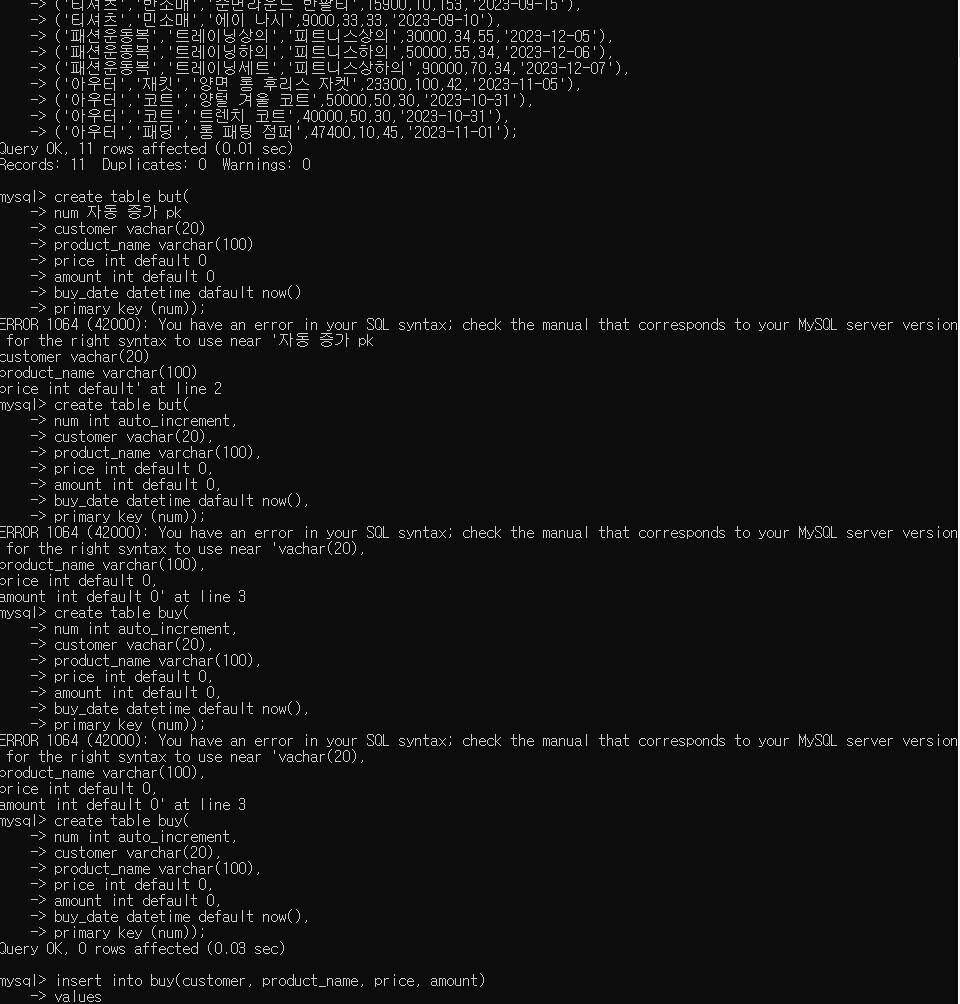
insert into product(type_a, type_b, name, price, amount, sale_amount, register_date) values
('티셔츠','긴소매','폴라 티셔츠',15000,34,100,'2023-10-15'),
('티셔츠','긴소매','크롭 티셔츠',10000,50,100,'2023-10-15'),
('티셔츠','반소매','순면라운드 반팔티',15900,10,153,'2023-09-15'),
('티셔츠','민소매','에이 나시',9000,33,33,'2023-09-10'),
('패션운동복','트레이닝상의','피트니스상의',30000,34,55,'2023-12-05'),
('패션운동복','트레이닝하의','피트니스하의',50000,55,34,'2023-12-06'),
('패션운동복','트레이닝세트','피트니스상하의',90000,70,34,'2023-12-07'),
('아우터','재킷','양면 롱 후리스 자켓',23300,100,42,'2023-11-05'),
('아우터','코트','양털 겨울 코트',50000,50,30,'2023-10-31'),
('아우터','코트','트렌치 코트',40000,50,30,'2023-10-31'),
('아우터','패딩','롱 패팅 점퍼',47400,10,45,'2023-11-01');
- 판매 테이블(buy)
create table buy(
num int auto_increment,
customer varchar(20),
product_name varchar(100),
price int default 0,
amount int default 0,
buy_date datetime default now(),
primary key (num));
---------------------------------------------
- 홍길동이 폴라 티셔츠 5개 구매
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
values
('홍길동', '폴라 티셔츠', 15000, 5);
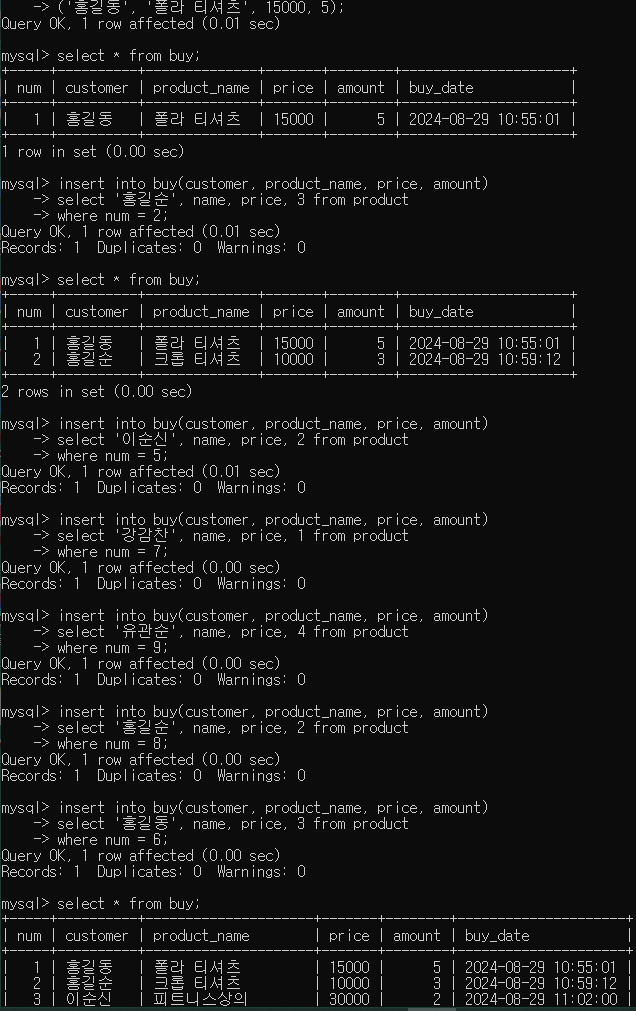
- product 테이블에서 제품 내용을 조회하여 추가
홍길순 크롭 티셔츠를 3장 구매(num = 2)
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '홍길순', name, price, 3 from product
where num = 2;
- 5명이 여러 가지 상품으로 구매
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '이순신', name, price, 2 from product
where num = 5;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '강감찬', name, price, 1 from product
where num = 7;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '유관순', name, price, 4 from product
where num = 9;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '홍길순', name, price, 2 from product
where num = 8;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '홍길동', name, price, 3 from product
where num = 6;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '김순이', name, price, 5 from product
where num = 2;
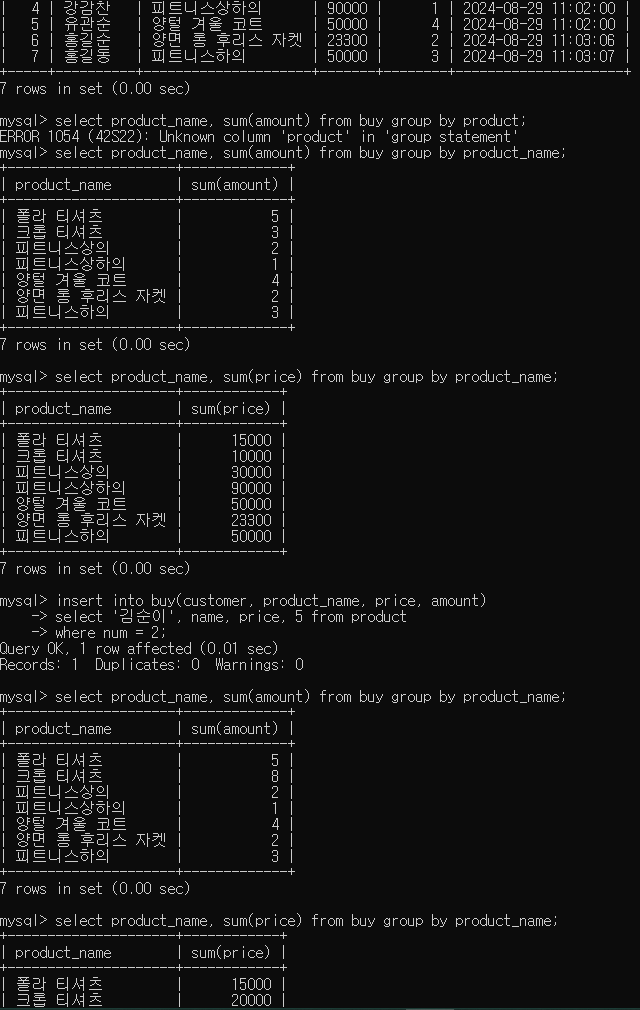
- 제품별 판매 수량 조회
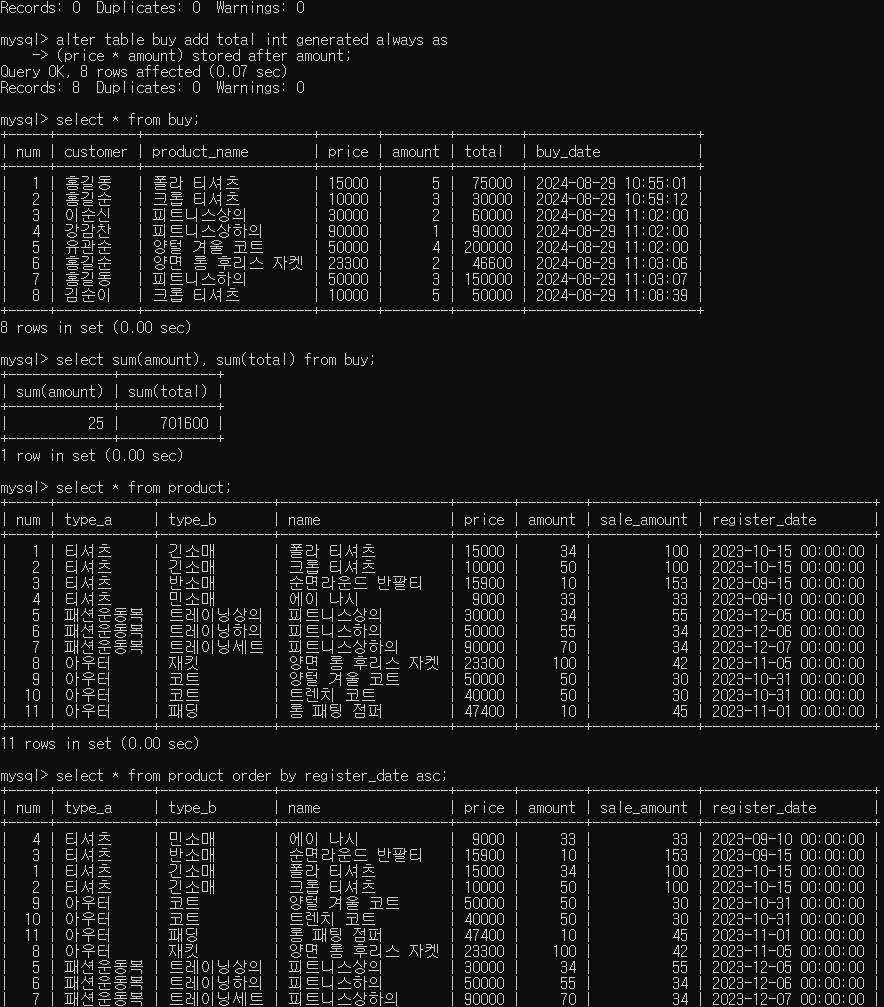
select product_name, sum(amount) from buy group by product_name;
- 제품별 판매 금액 조회
select product_name, sum(price) from buy group by product_name;
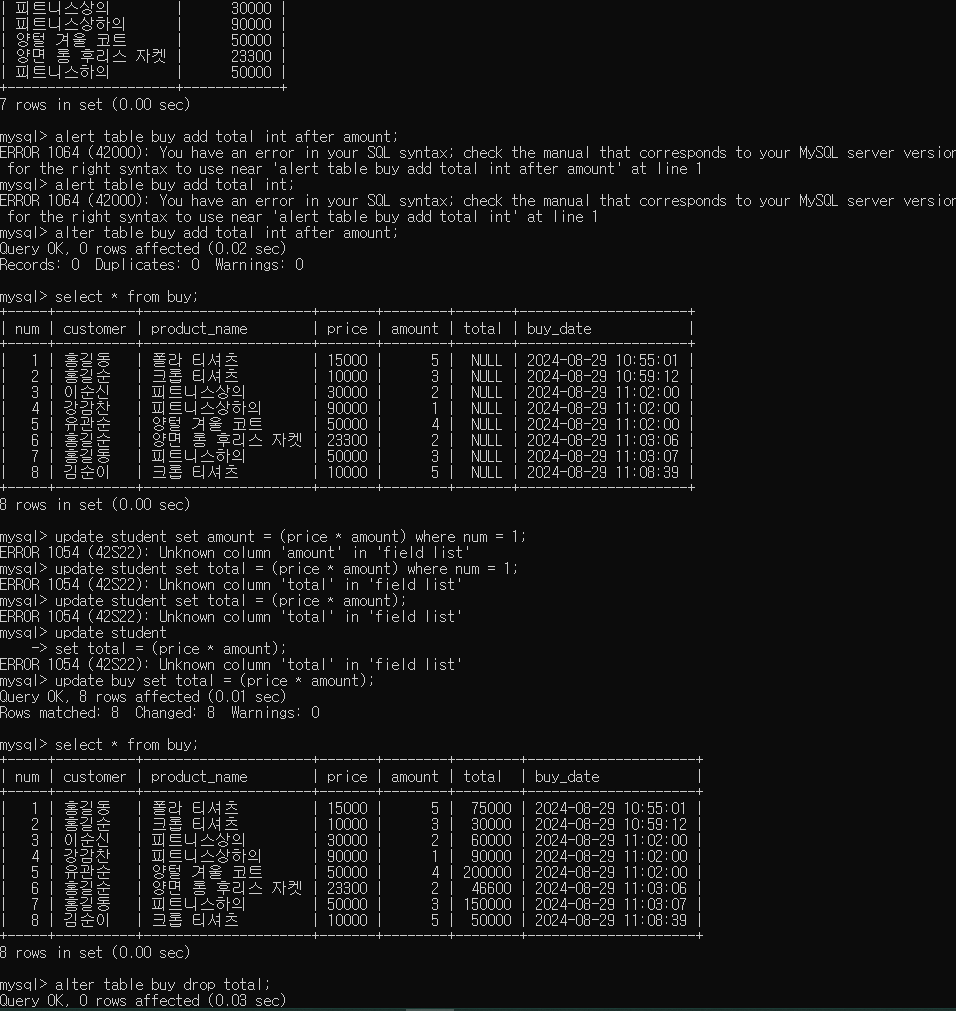
- total 필드를 추가 int
alter table buy add total int after amount;
- price * amount 곱한 값으로 나타내기
update buy set total = (price * amount);
- 칼럼을 생성 시 계산된 값을 자동 계산하여 생성
(generated columns)
- stored : 값이 저장되는 방식
=> 데이터가 입력되거나 수정될 때 해당 칼럼도 같이 갱신
- virtual : 데이터를 저장하지 않고 정의만
=> 해당 칼럼을 읽으려고 시도할 때 계산을 통해 보여주는 것만
- 방금 전 생성한 total 필드를 삭제하고, 다시 generated columns으로 추가
alter table buy drop total;
alter table buy add total int generated always as
(price * amount) stored after amount;
- 전체 총 판매수량과 총 매출액 출력
select sum(amount), sum(total) from buy;
-----------------------------------------------
- 과제 1
- product 테이블에서
1. 최신 상품순으로 정렬
select * from product order by register_date desc;
2. type_a 별로 상품의 개수와 price 합계
select type_a, count(type_a) as '상품 개수', sum(price) as '합계' from product group by type_a;
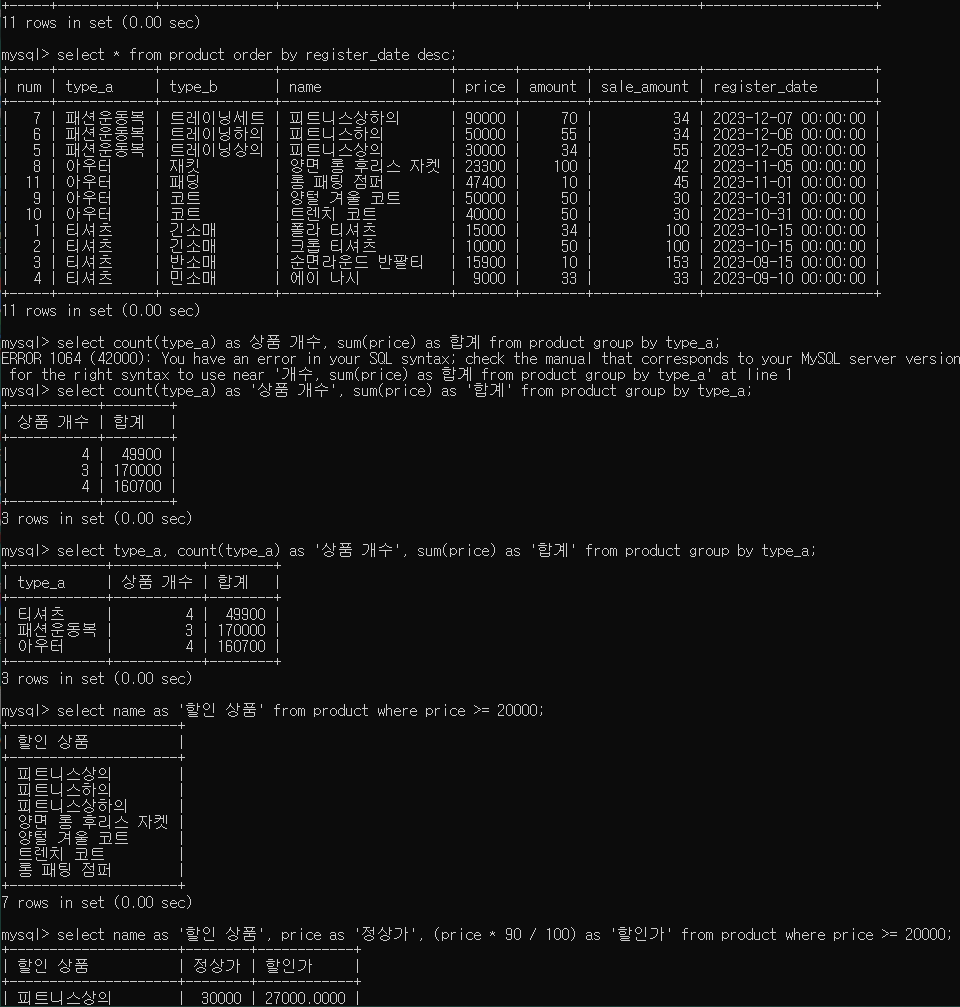
3. price 20000이상인 제품은 할인 상품에 해당. 할인 상품을 출력
select name as '할인 상품' from product where price >= 20000;
4. 할인 상품의 이름과 가격을 출력
-- 할인 가격(2만원 이상인 제품만 대상으로 10% 할인된 가격)
-- 할인 상품명, 정상가, 할인가
select name as '할인 상품', price as '정상가', round((price * 90 / 100),0) as '할인가' from product where price >= 20000;
- 모든 데이터의 이름, 정상가, 할인가 출력
(할인 대상 상품(5만원)이 아니라면 할인가 = 정상가)
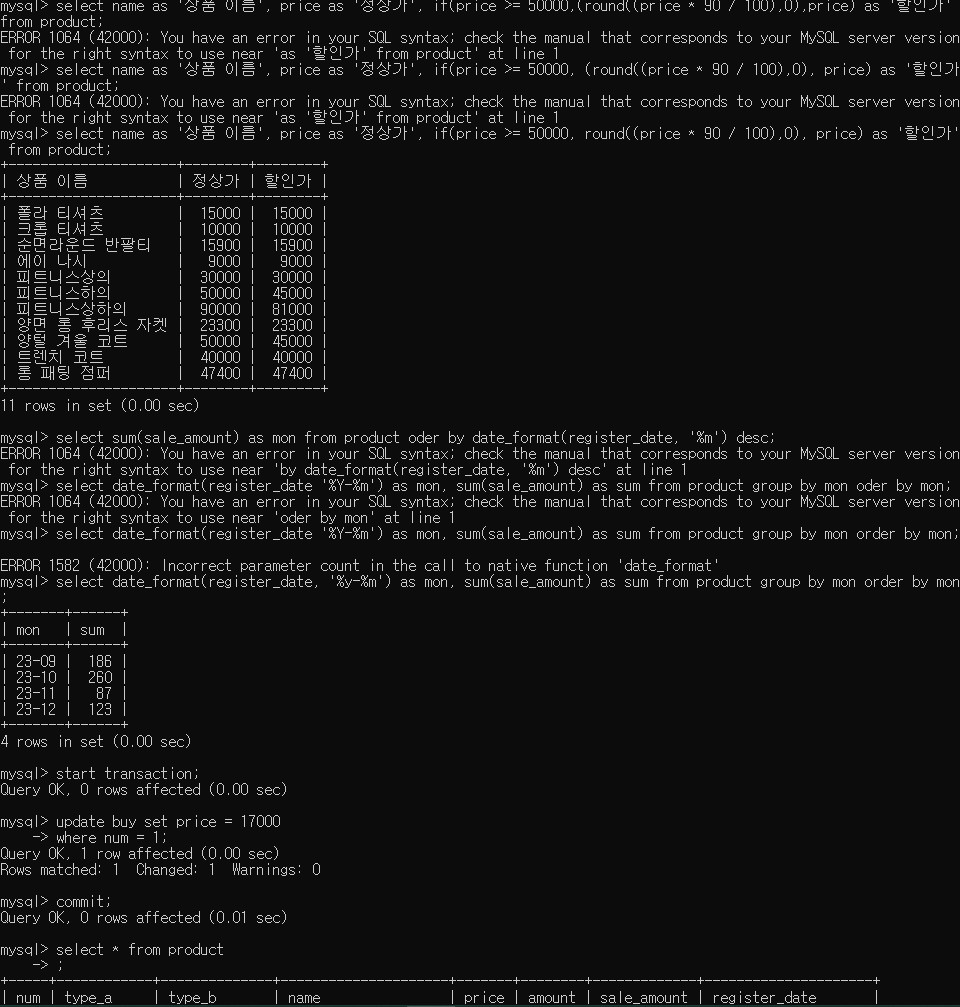
select name as '상품 이름', price as '정상가', if(price >= 50000, round((price * 90 / 100),0), price) as '할인가' from product;
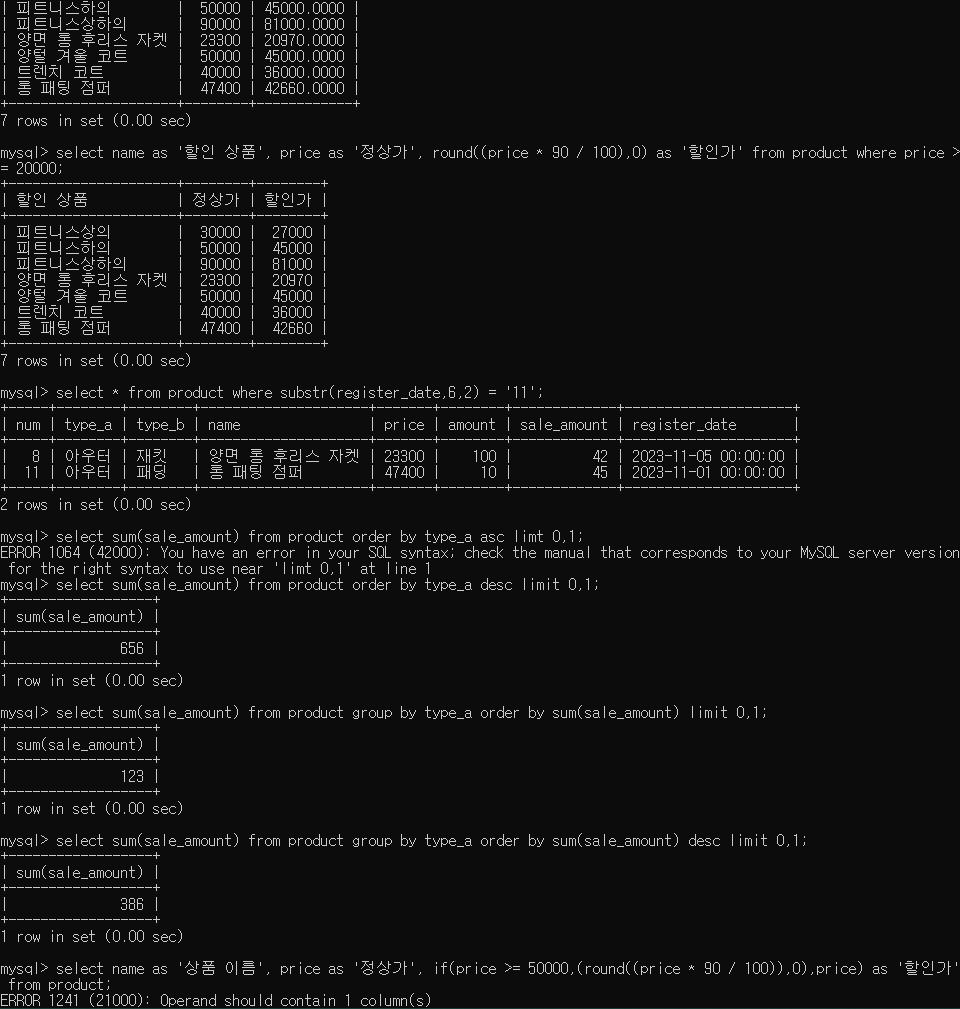
5. 11월에 입력된 상품만 출력
select * from product where substr(register_date,6,2) = '11';
date_format : %y (년도 2자리) %Y(년도 4자리)
select date_format(register_date, '%y-%m') as mon from product;
- 월별 판매수량(sale_amount) 합계 / 월별로 오름차순 정렬
select date_format(register_date, '%y-%m') as mon, sum(sale_amount) as sum from product group by mon order by mon;
6. type_a 별로 판매량(sale_amount) 합계가 가장 큰 값를 출력
select type_a, sum(sale_amount) as sum from product group by type_a order by sum desc limit 1;
--서브쿼리 사용 (서브쿼리의 값을 이용할 경우 별칭(alias)은 필수)
select avg(sum) from (select sum(sale_amount) as sum from product group by type_a) p;
-----------------------------------------------------------
트랜잭션 (transaction)
- 하나의 작업을 하기 위한 명령어 묶음 단위
- 하나의 트랜잭션에서 실행하는 모든 명령어가 완료되어야
전체가 완련되는 형태의 작업에서 사용
- 만약 하나라도 작업이 취소되면 모두 취소
- 완료와 취소를 나중에 결정하는 개념
- 임시 실행 개념
- 데이터의 안정성을 확보학 위한 방법
start transaction;
명령어 1;
명령어 2;
...
commit; => 완료
rollback; => 취소
DDL(create, drop, alter, rename) => rollback 대상이 아님
- mysql에서는 auto commit이 기본적으로 on 상태
트랜잭션을 이용하여
start transaction;
1. 폴라 티셔츠 가격을 15000 => 17000 변경
update buy set price = 17000
where num = 1;
2. 변경된 값을 확인
select * from buy;
rollback;
-------------------------
1. buy 테이블에서 customer의 이름을 홍O동 변경하여 출력 (select)
select num, insert(customer,2,1,'O'), from buy;
2. product 테이블에서 price가 4만원 이상인 데이터만 조회
상품명(할인상품) 표시하여 출력 (전체데이터 표시)
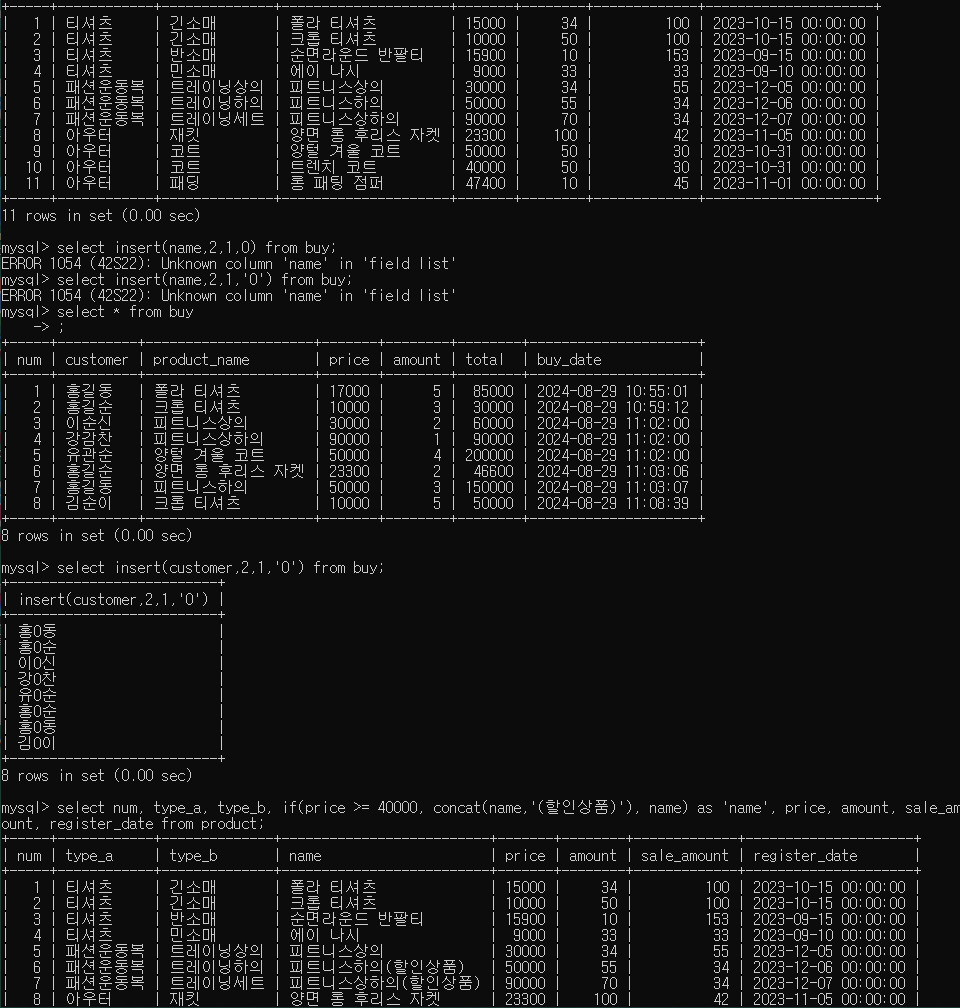
select num, type_a, type_b, if(price >= 40000, concat(name,'(할인상품)'), name) as 'name', price, amount, sale_amount, register_date from product;
3. product 테이블에서 월별 매출(price * sale_amount) 합계 출력
select month(register_date) as mon, sum(price * sale_amount) as sum from product group by mon order by mon;
4. product 테이블에서 price가 가장 큰(가장 비싼) 제품명, price 출력
select name, price from product where prcie = (select max(price) from product);
5. buy 테이블의 구매 내역 3개 추가
=> (product 테이블을 조회하여 추가)
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '이순신', name, price, 2 from product
where num = 5;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '강감찬', name, price, 1 from product
where num = 7;
insert into buy(customer, product_name, price, amount)
select '유관순', name, price, 4 from product
where num = 9;
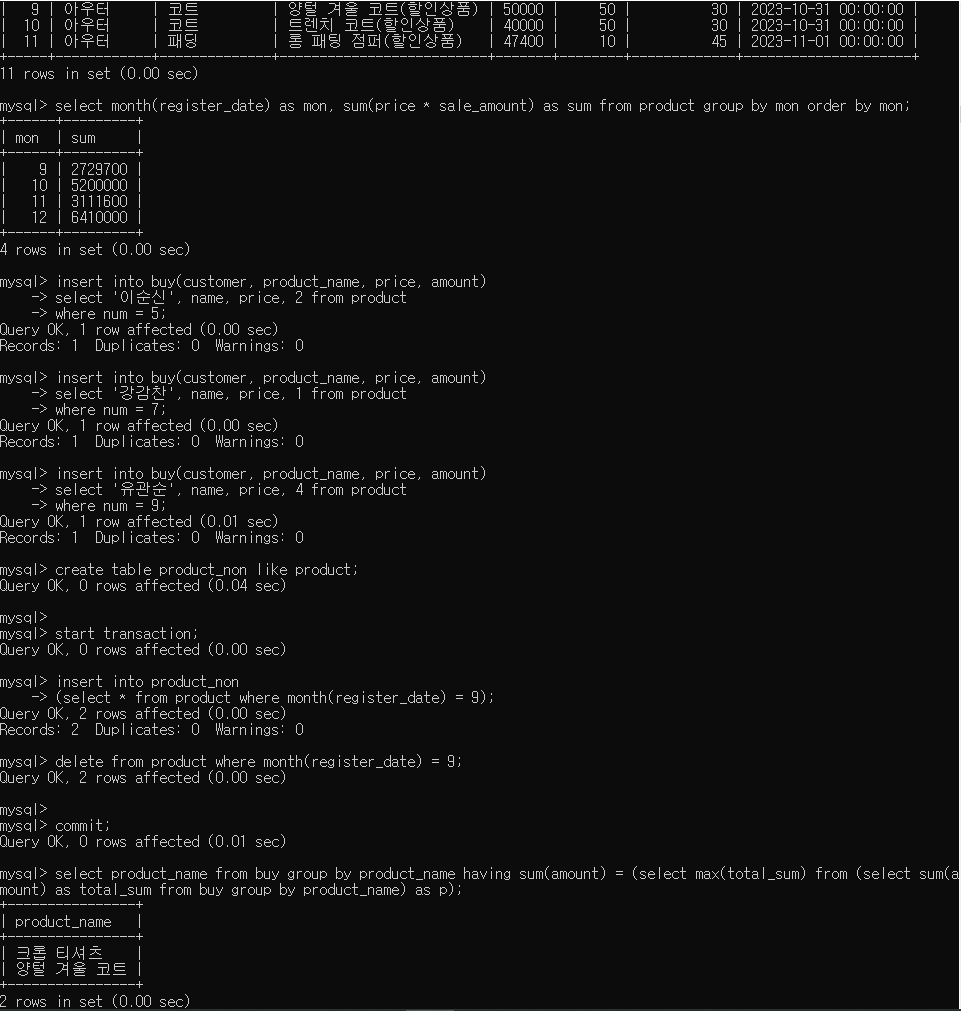
6. product_non 테이블을 prduct 테이블과 같은 형식으로 추가하여 register_dae의 9월 데이터 이동
=> 기존 product 테이블에서 제거
=> transaction을 이용하여 첫 과정 부터완료되었을 commit하기
create table product_non like product;
start transaction;
insert into product_non
(select * from product where month(register_date) = 9);
delete from product where month(register_date) = 9;
commit;
7. buy 테이블에서 가장 많이 판매한 제품의 이름 출력
select product_name, sum(amount) as sum from buy
group by product_name
oreder by sum desc
limit 1;
select product_name from buy
group by product_name having sum(amount) =
(select max(total_sum) from
(select sum(amount) as total_sum from buy
group by product_name) as p);
▷ 출력
2. ERD
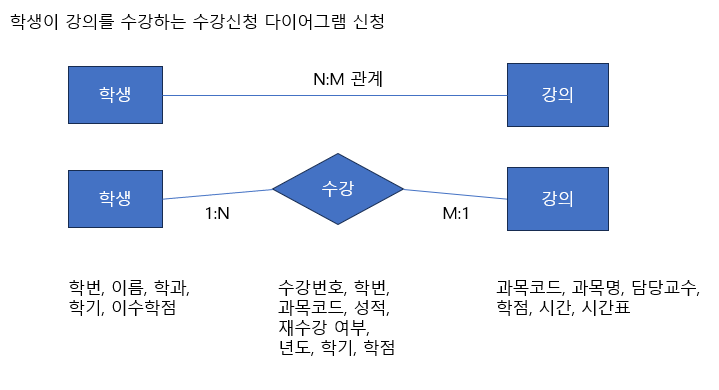
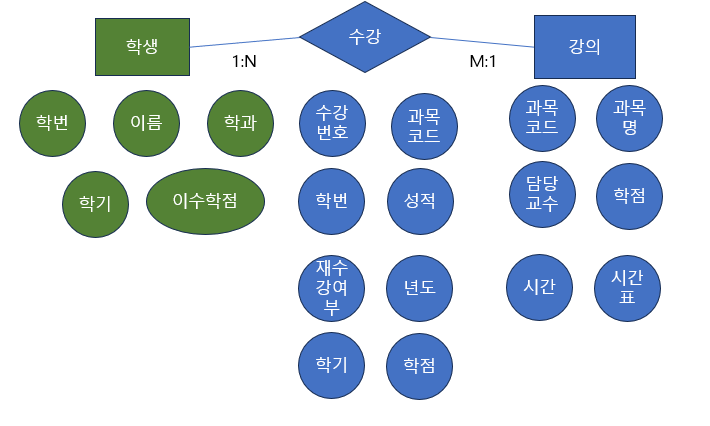
◈ ERD


-----------------------------------------------------------
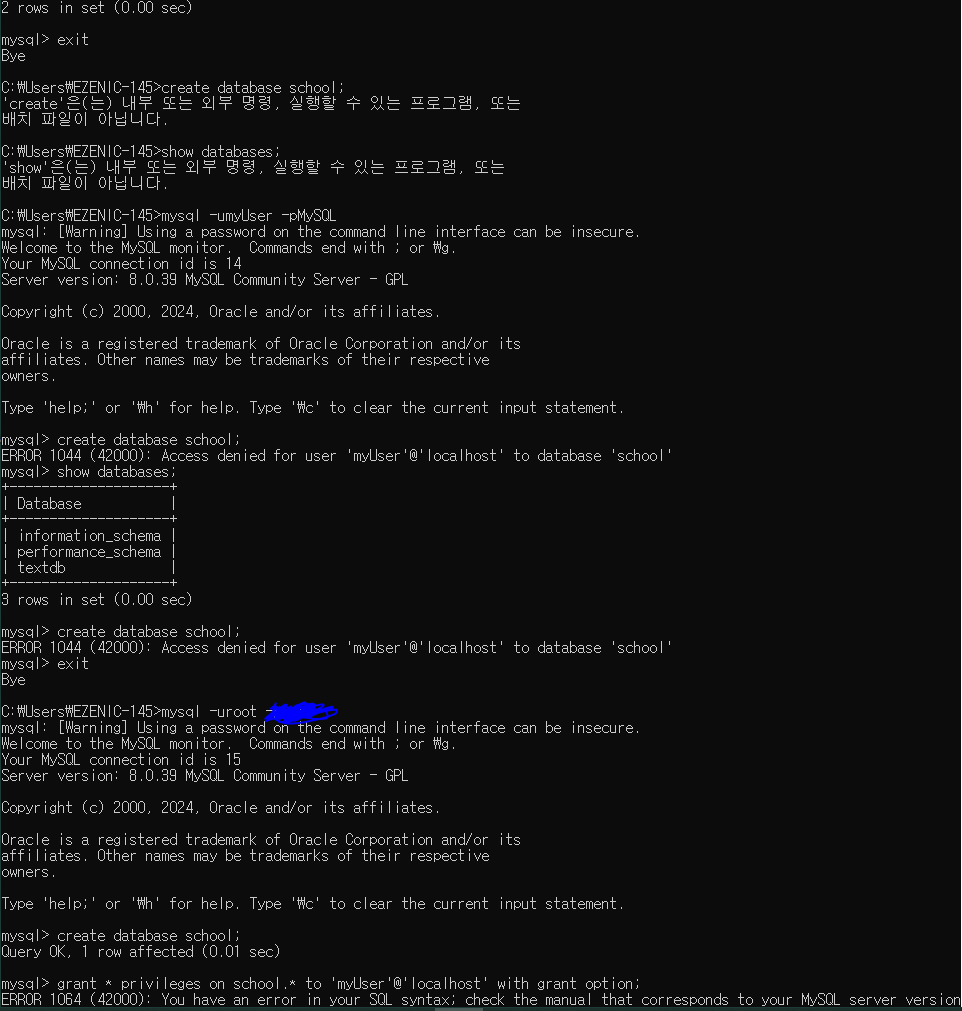
DB 생성 - root 계정에서 생성
myUser => 생성한 DB를 사용할 수 있는 권한 부여
DB명 => school (student, attend, course 테이블 생성)
1. root 계정으로 접속
mysql -uroot -p비밀번호
2. create database school; => db 생성
create database school;
3. myUser 권한 부여 => 권한 확정
grant all privileges on school.* to 'myUser'@'localhost' with grant option;
flush privileges;
4. myUser 계정으로 접속
mysql -umyUser -pMySQL
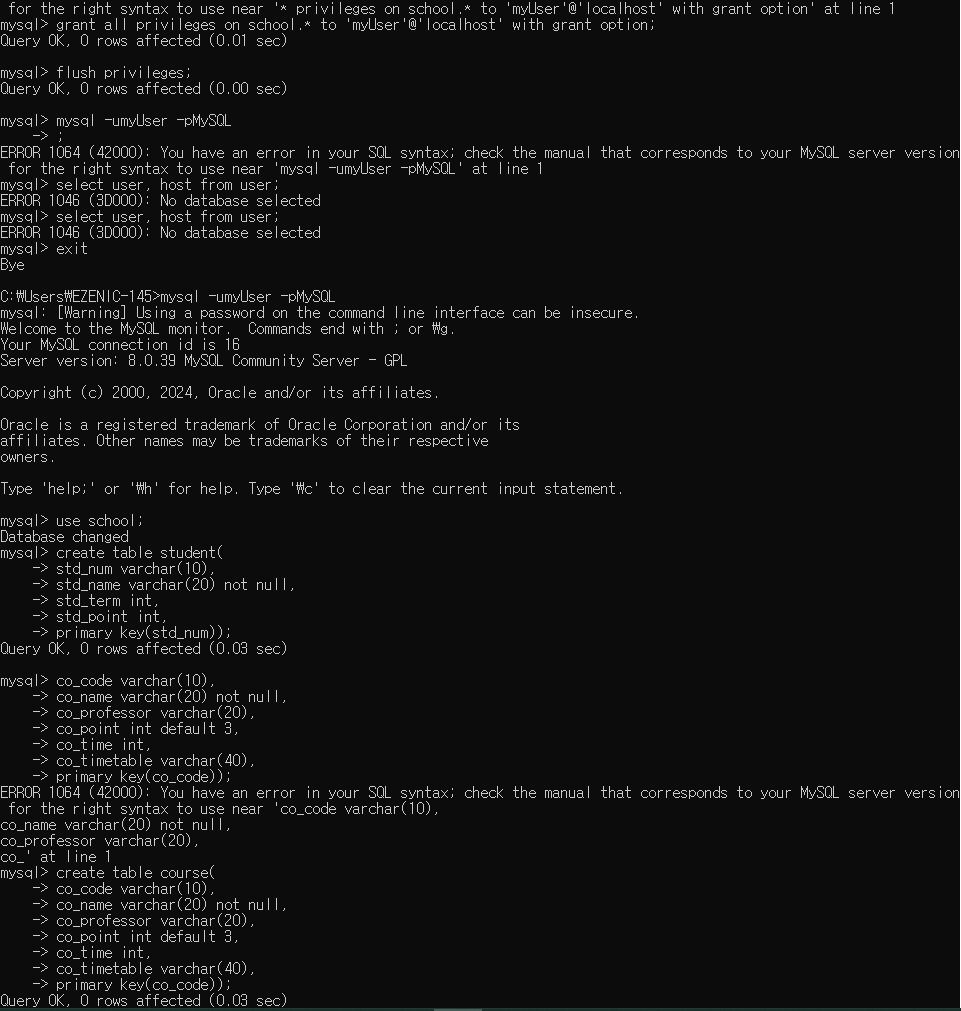
use school;
5. 테이블 3개 생성
create table student(
std_num varchar(10),
std_name varchar(20) not null,
std_term int,
std_point int,
primary key(std_num));
create table course(
co_code varchar(10),
co_name varchar(20) not null,
co_professor varchar(20),
co_point int default 3,
co_time int,
co_timetable varchar(40),
primary key(co_code));
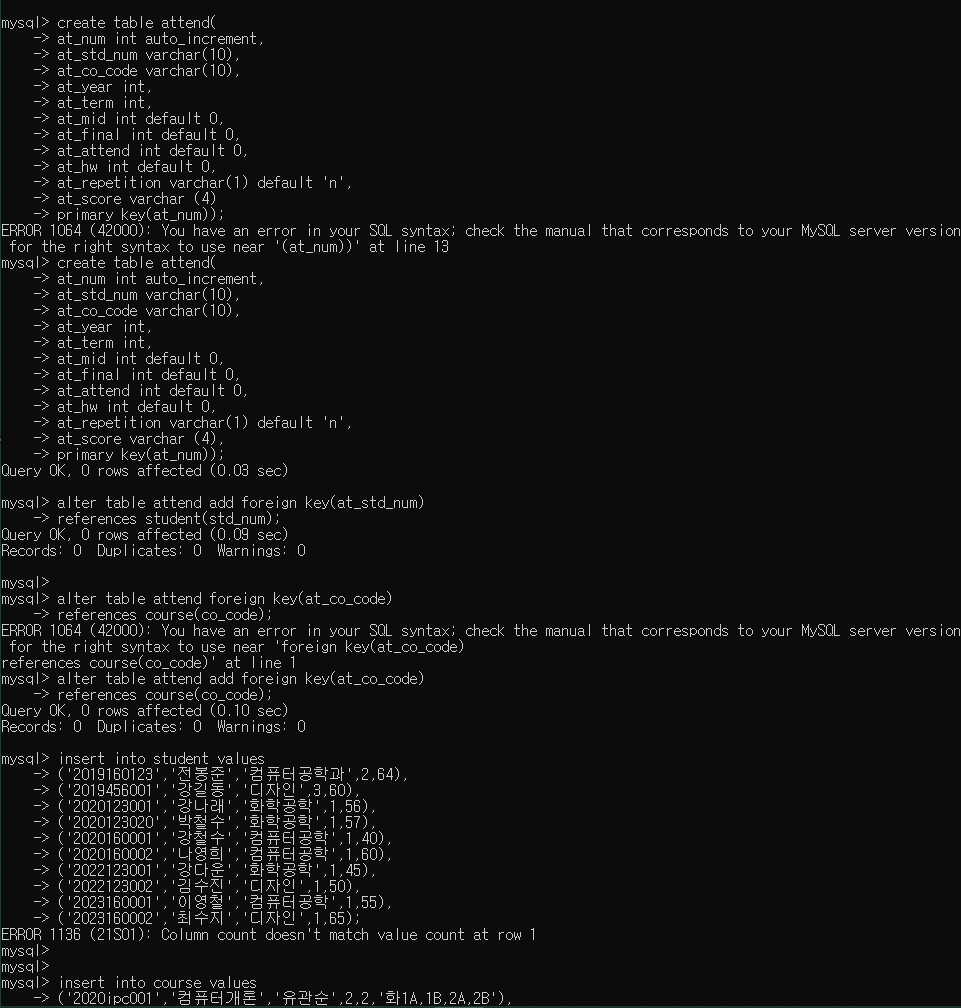
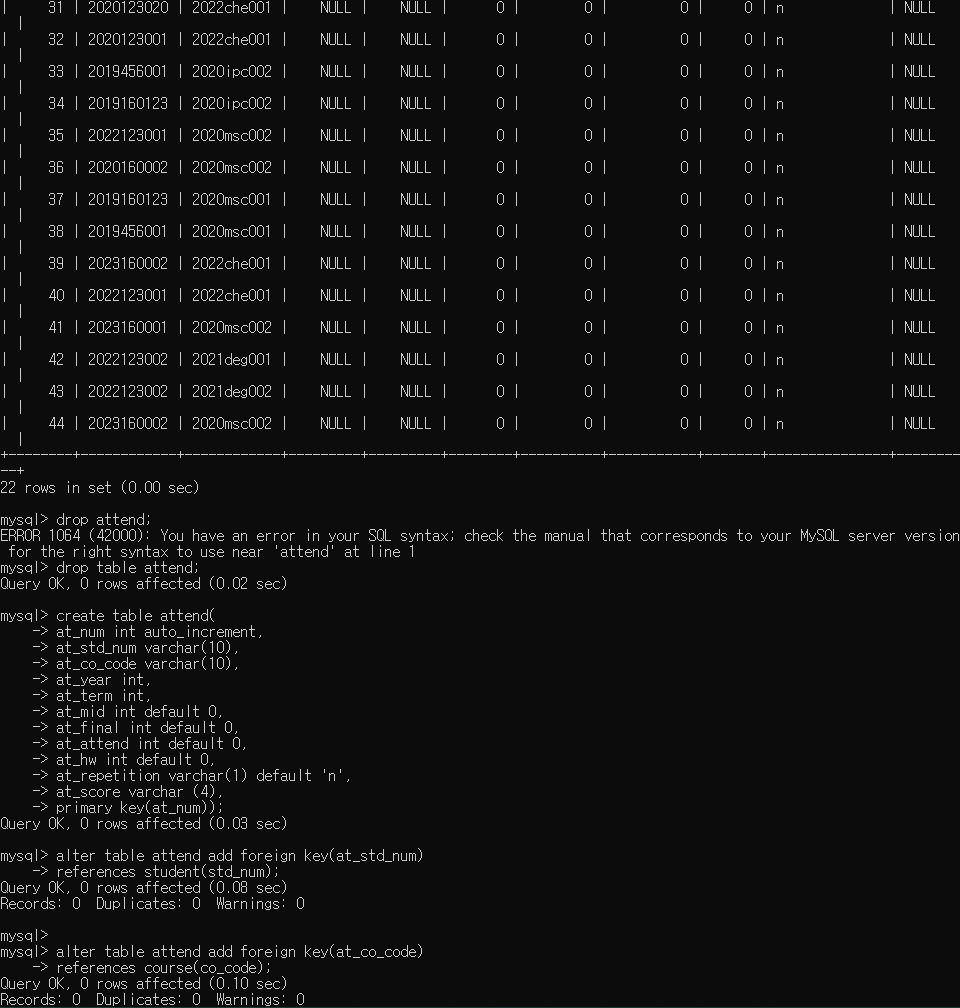
create table attend(
at_num int auto_increment,
at_std_num varchar(10),
at_co_code varchar(10),
at_year int,
at_term int,
at_mid int default 0,
at_final int default 0,
at_attend int default 0,
at_hw int default 0,
at_repetition varchar(1) default 'n',
at_score varchar (4),
primary key(at_num));
6. 외래키 지정
alter table attend add foreign key(at_std_num)
references student(std_num);
alter table attend add foreign key(at_co_code)
references course(co_code);
7. DB자료
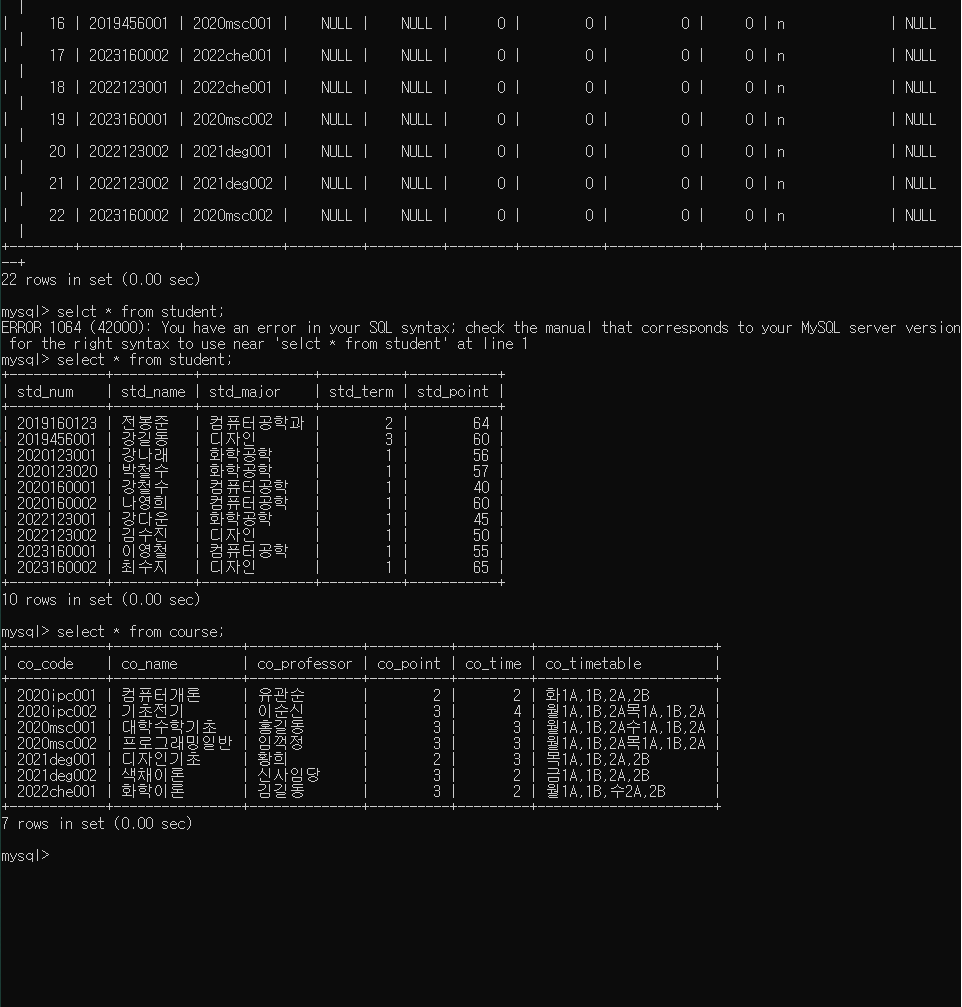
insert into student values
('2019160123','전봉준','컴퓨터공학과',2,64),
('2019456001','강길동','디자인',3,60),
('2020123001','강나래','화학공학',1,56),
('2020123020','박철수','화학공학',1,57),
('2020160001','강철수','컴퓨터공학',1,40),
('2020160002','나영희','컴퓨터공학',1,60),
('2022123001','강다운','화학공학',1,45),
('2022123002','김수진','디자인',1,50),
('2023160001','이영철','컴퓨터공학',1,55),
('2023160002','최수지','디자인',1,65);
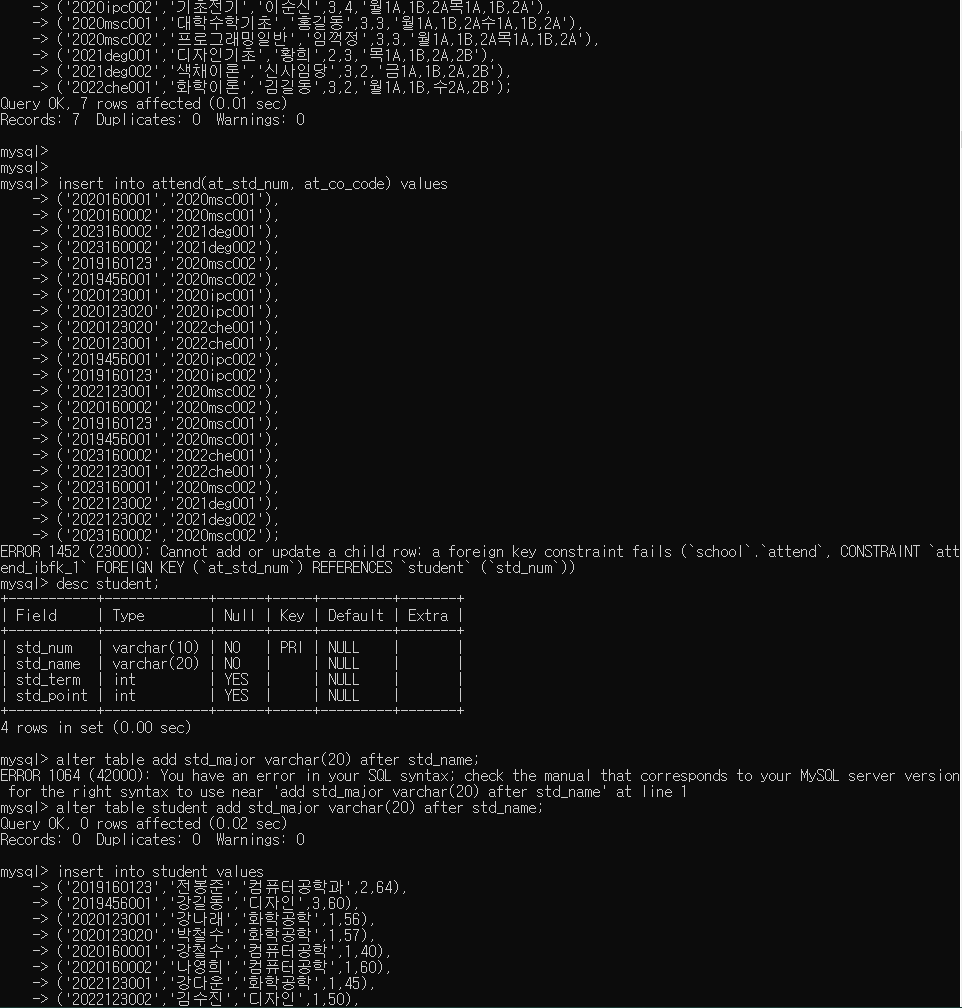
insert into course values
('2020ipc001','컴퓨터개론','유관순',2,2,'화1A,1B,2A,2B'),
('2020ipc002','기초전기','이순신',3,4,'월1A,1B,2A목1A,1B,2A'),
('2020msc001','대학수학기초','홍길동',3,3,'월1A,1B,2A수1A,1B,2A'),
('2020msc002','프로그래밍일반','임꺽정',3,3,'월1A,1B,2A목1A,1B,2A'),
('2021deg001','디자인기초','황희',2,3,'목1A,1B,2A,2B'),
('2021deg002','색채이론','신사임당',3,2,'금1A,1B,2A,2B'),
('2022che001','화학이론','김길동',3,2,'월1A,1B,수2A,2B');
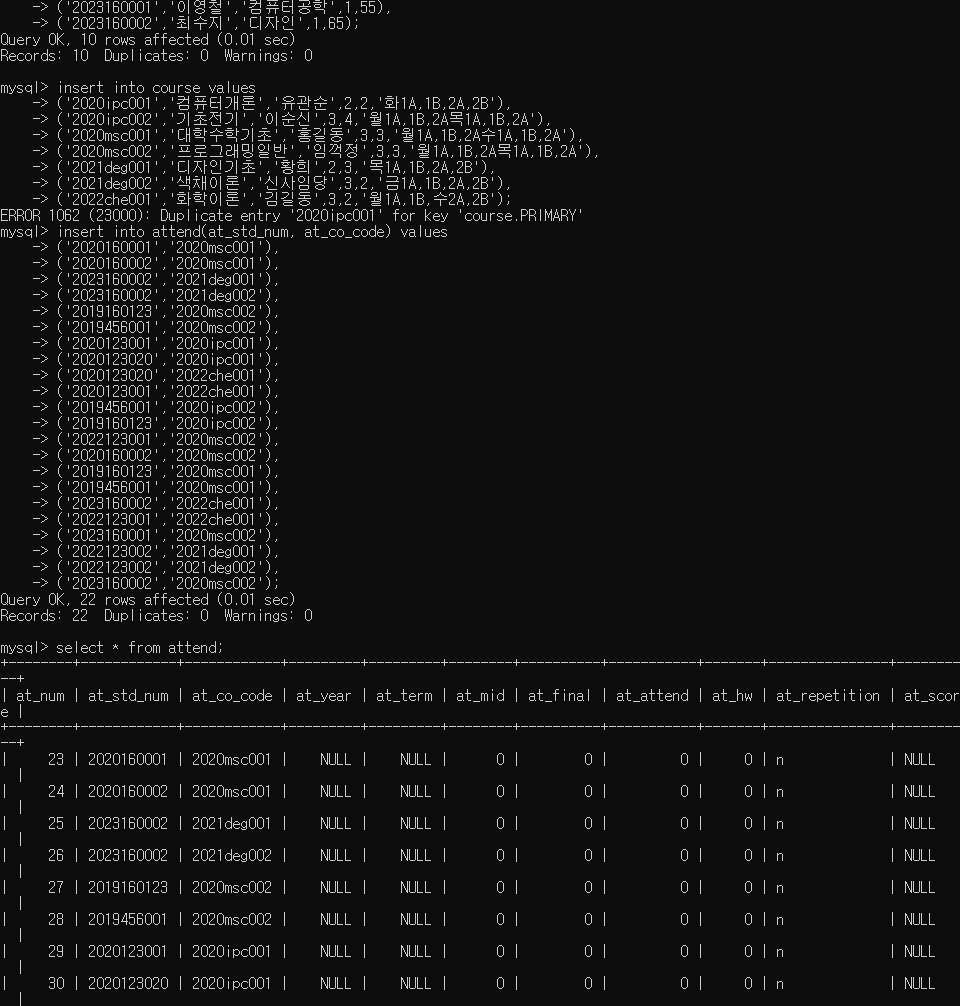
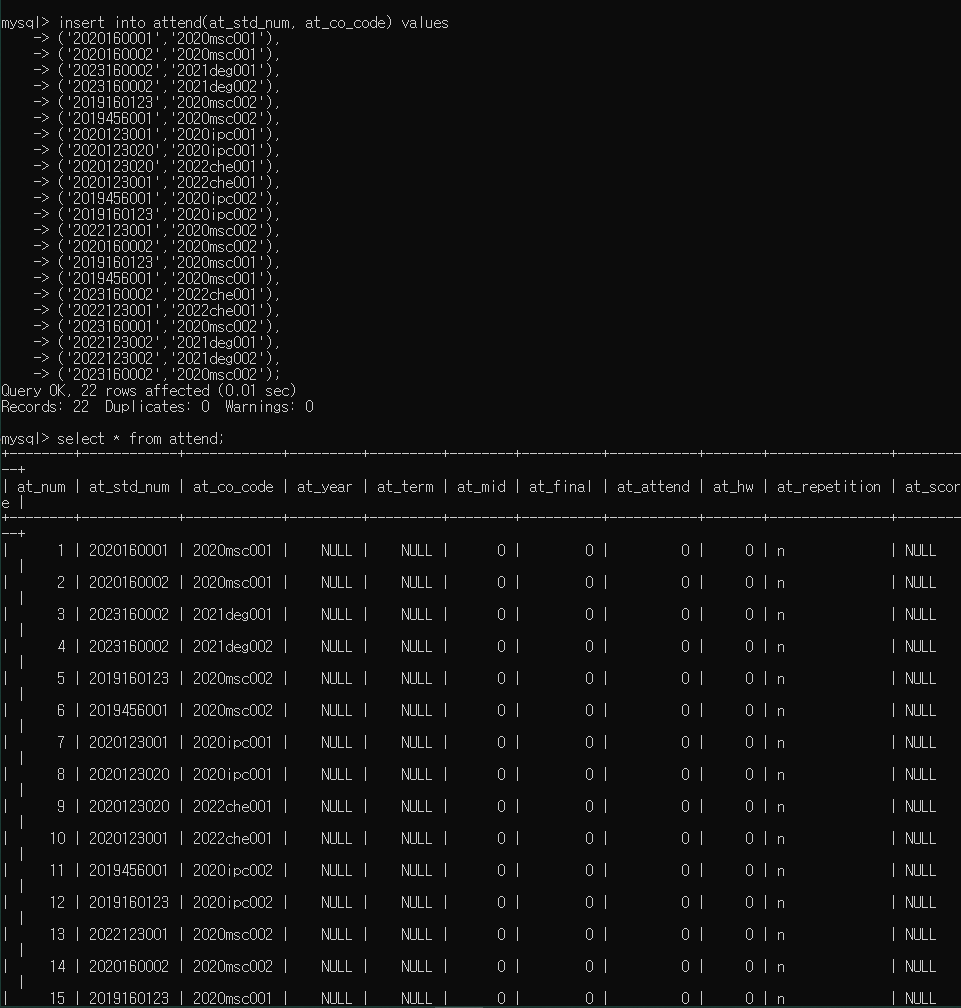
insert into attend(at_std_num, at_co_code) values
('2020160001','2020msc001'),
('2020160002','2020msc001'),
('2023160002','2021deg001'),
('2023160002','2021deg002'),
('2019160123','2020msc002'),
('2019456001','2020msc002'),
('2020123001','2020ipc001'),
('2020123020','2020ipc001'),
('2020123020','2022che001'),
('2020123001','2022che001'),
('2019456001','2020ipc002'),
('2019160123','2020ipc002'),
('2022123001','2020msc002'),
('2020160002','2020msc002'),
('2019160123','2020msc001'),
('2019456001','2020msc001'),
('2023160002','2022che001'),
('2022123001','2022che001'),
('2023160001','2020msc002'),
('2022123002','2021deg001'),
('2022123002','2021deg002'),
('2023160002','2020msc002');
▷ 출력
3. 예제 문제
▣ 문제
▷ 1번
- product 테이블에서
1. 최신 상품순으로 정렬
2. type_a 별로 상품의 개수와 price 합계
3. price 20000이상인 제품은 할인 상품에 해당. 할인 상품을 출력
4. 할인 상품의 이름과 가격을 출력
-- 할인 가격(2만원 이상인 제품만 대상으로 10% 할인된 가격)
-- 할인 상품명, 정상가, 할인가
- 모든 데이터의 이름, 정상가, 할인가 출력
(할인 대상 상품(5만원)이 아니라면 할인가 = 정상가)
5. 11월에 입력된 상품만 출력
6. type_a 별로 판매량(sale_amount) 합계가 가장 큰 값를 출력
▣ 정답
▷ 1번
- product 테이블에서
1. 최신 상품순으로 정렬
select * from product order by register_date desc;
2. type_a 별로 상품의 개수와 price 합계
select type_a, count(type_a) as '상품 개수', sum(price) as '합계' from product group by type_a;
3. price 20000이상인 제품은 할인 상품에 해당. 할인 상품을 출력
select name as '할인 상품' from product where price >= 20000;
4. 할인 상품의 이름과 가격을 출력
-- 할인 가격(2만원 이상인 제품만 대상으로 10% 할인된 가격)
-- 할인 상품명, 정상가, 할인가
select name as '할인 상품', price as '정상가', round((price * 90 / 100),0) as '할인가' from product where price >= 20000;
- 모든 데이터의 이름, 정상가, 할인가 출력
(할인 대상 상품(5만원)이 아니라면 할인가 = 정상가)
select name as '상품 이름', price as '정상가', if(price >= 50000, round((price * 90 / 100),0), price) as '할인가' from product;
5. 11월에 입력된 상품만 출력
select * from product where substr(register_date,6,2) = '11';
date_format : %y (년도 2자리) %Y(년도 4자리)
select date_format(register_date, '%y-%m') as mon from product;
- 월별 판매수량(sale_amount) 합계 / 월별로 오름차순 정렬
select date_format(register_date, '%y-%m') as mon, sum(sale_amount) as sum from product group by mon order by mon;
6. type_a 별로 판매량(sale_amount) 합계가 가장 큰 값를 출력
select type_a, sum(sale_amount) as sum from product group by type_a order by sum desc limit 1;
--서브쿼리 사용 (서브쿼리의 값을 이용할 경우 별칭(alias)은 필수)
select avg(sum) from (select sum(sale_amount) as sum from product group by type_a) p;
4. 느낀 점
ERD에 대한 이론을 배우게 되면서 DB에 대해 한 발짝 다가간 것 같아서 기쁘다.
'DB > MySQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MySQL 기초(trigger)- AWS 풀스택 과정 35일차 (0) | 2024.09.02 |
|---|---|
| MySQL 기초(join, rollup, rank)- AWS 풀스택 과정 34일차 (0) | 2024.08.30 |
| MySQL 기초(DML)- AWS 풀스택 과정 32일차 (0) | 2024.08.28 |
| MySQL 기초(DB기초)- AWS 풀스택 과정 31일차 (0) | 2024.08.27 |
| MySQL 설정 및 기초- AWS 풀스택 과정 30일차 (0) | 2024.08.26 |